|
|
| (2人の利用者による、間の45版が非表示) |
| 1行目: |
1行目: |
| <div align="right">
| |
| <font size="+1">[https://researchmap.jp/read0206369 橋本 謙二]</font><br>
| |
| ''千葉大学 社会精神保健教育研究センター''<br>
| |
| DOI:<selfdoi /> 原稿受付日:2020年8月5日 原稿完成日:2020年8月25日<br>
| |
| 担当編集委員:[http://researchmap.jp/tadafumikato 加藤 忠史](順天堂大学大学院医学研究科 精神・行動科学/医学部精神医学講座)<br>
| |
| </div>
| |
|
| |
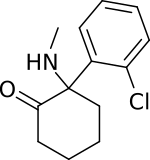
| 英:ketamine 独:Ketamin 仏:kétamine
| |
|
| |
| {{box|text= アリルシクロヘキシルアミン系の解離性麻酔薬であり、世界保健機関による必須医薬品の一つである。薬物乱用が問題になり麻薬指定された。精神医学領域では、ケタミンは統合失調症モデルとして使用されているが、近年、ケタミンの即効性抗うつ効果が注目されている。}}
| |
| {{Drugbox | | {{Drugbox |
| | Watchedfields = changed | | | Watchedfields = changed |
| 25行目: |
15行目: |
| | licence_US = Ketamine | | | licence_US = Ketamine |
| | pregnancy_AU = B3 | | | pregnancy_AU = B3 |
| | pregnancy_AU_comment = <ref name="Drugs.com pregnancy">https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/ketamine.html</ref> | | | pregnancy_AU_comment = <ref name="Drugs.com pregnancy">{{cite web | title=Ketamine (Ketalar) Use During Pregnancy | website=Drugs.com | date=22 November 2019 | url=https://www.drugs.com/pregnancy/ketamine.html | access-date=18 May 2020}}</ref> |
| | pregnancy_US = N | | | pregnancy_US = N |
| | pregnancy_US_comment = <ref name="Drugs.com pregnancy" /> | | | pregnancy_US_comment = <ref name="Drugs.com pregnancy" /> |
| 34行目: |
24行目: |
| | legal_US = Schedule III | | | legal_US = Schedule III |
| | legal_UN = Unscheduled | | | legal_UN = Unscheduled |
| | routes_of_administration = Any<ref><pubmed>28657160</pubmed></ref><ref><pubmed> 28339431 </pubmed></ref><ref name="MathewZarate2016"><pubmed>24257811 </pubmed></ref> | | | routes_of_administration = Any<ref><pubmed>28657160</pubmed></ref><ref><pubmed> 28339431 </pubmed></ref><ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref name="MD" /> |
| | addiction_liability = Low–moderate<ref name="NHM-PCP and ketamine">'''Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE'''<br>Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders |quote=Phencyclidine (PCP or angel dust) and ketamine (also known as special K) are structurally related drugs... their reinforcing properties and risks related to compulsive abuse<br>edited by Sydor A, Brown RY, Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience 2nd ed. pp. 374–375 (2009) McGraw-Hill Medical, New York</ref><!--Start widen drugbox--><br /> <!--End widen drugbox--> | | | addiction_liability = Low–moderate<ref name="NHM-PCP and ketamine">{{cite book |vauthors=Malenka RC, Nestler EJ, Hyman SE |veditors=Sydor A, Brown RY |title=Molecular Neuropharmacology: A Foundation for Clinical Neuroscience |year=2009 |publisher=McGraw-Hill Medical |location=New York |isbn=978-0-07-148127-4 | pages=374–375 |edition=2nd |chapter=Chapter 15: Reinforcement and Addictive Disorders |quote=Phencyclidine (PCP or angel dust) and ketamine (also known as special K) are structurally related drugs... their reinforcing properties and risks related to compulsive abuse}}</ref><!--Start widen drugbox--><br /> <!--End widen drugbox--> |
| | class = [[NMDA receptor antagonists]]; [[General anesthetics]]; [[Dissociative hallucinogen]]s; [[Analgesic]]s; [[Antidepressant]]s | | | class = [[NMDA receptor antagonists]]; [[General anesthetics]]; [[Dissociative hallucinogen]]s; [[Analgesic]]s; [[Antidepressant]]s |
|
| |
|
| 42行目: |
32行目: |
| * [[Intravenous therapy|Intravenous]]: 100%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /> | | * [[Intravenous therapy|Intravenous]]: 100%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /> |
| * [[Intramuscular injection|Intramuscular]]: 93%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /> | | * [[Intramuscular injection|Intramuscular]]: 93%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /> |
| * [[Subcutaneous injection|Subcutaneous]]: high<ref name="Mao2016">'''Jianren Mao. (2016).'''<br>Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia <br>CRC Press</ref> | | * [[Subcutaneous injection|Subcutaneous]]: high<ref name="Mao2016">{{cite book |author=Jianren Mao |title=Opioid-Induced Hyperalgesia |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_VrvBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA127 |date=19 April 2016 |publisher=CRC Press |isbn=978-1-4200-8900-4 |pages=127– |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170908185726/https://books.google.com/books?id=_VrvBQAAQBAJ&pg=PA127 |archivedate=8 September 2017 }}</ref> |
| * [[Epidural administration|Epidural]]: 77%<ref name="Kintz2014">'''Pascal Kintz. (2014).'''<br>Toxicological Aspects of Drug-Facilitated Crimes<br>Elsevier Science</ref> | | * [[Epidural administration|Epidural]]: 77%<ref name="Kintz2014">{{cite book |author=Pascal Kintz |title=Toxicological Aspects of Drug-Facilitated Crimes |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=YgnUAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA87 |date=22 March 2014 |publisher=Elsevier Science |isbn=978-0-12-416969-2 |pages=87– |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170908185726/https://books.google.com/books?id=YgnUAgAAQBAJ&pg=PA87 |archivedate=8 September 2017 }}</ref> |
| * [[Intranasal administration|Intranasal]]: 8–50%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref name="pmid29736744"><pubmed> 29736744</pubmed></ref><ref name="sinner"><pubmed> 18175098 </pubmed></ref> | | * [[Intranasal administration|Intranasal]]: 8–50%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref name="pmid29736744"> 29736744</ref><ref name="sinner" /> |
| * [[Sublingual administration|Sublingual]]: 24–30%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref name="Hashimoto2019"><pubmed>31215725</pubmed></ref> | | * [[Sublingual administration|Sublingual]]: 24–30%<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref name="Hashimoto2019"><pubmed>31215725</pubmed></ref> |
| * [[Rectal administration|Rectal]]: 11–30%<ref name="Nemeroff2017"> | | * [[Rectal administration|Rectal]]: 11–30%<ref name="Nemeroff2017">{{cite book |author1=Alan F. Schatzberg |author2=Charles B. Nemeroff |title=The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology, Fifth Edition |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KfHEDgAAQBAJ&pg=PA550 |year=2017 |publisher=American Psychiatric Pub |isbn=978-1-58562-523-9 |pages=550– |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170908185726/https://books.google.com/books?id=KfHEDgAAQBAJ&pg=PA550 |archivedate=8 September 2017 }}</ref><ref name=Zhang2018 /> |
| '''Alan F. Schatzberg & Charles B. Nemeroff. (2017).'''<br>The American Psychiatric Association Publishing Textbook of Psychopharmacology, Fifth Edition<br>American Psychiatric Pub, pp550-.</ref>
| | * [[Oral administration|By mouth]]: 16–29%<ref name="Kintz2014" /><ref name="DickmanSchneider2016">{{cite book |author1=Andrew Dickman |author2=Jennifer Schneider |title=The Syringe Driver: Continuous Subcutaneous Infusions in Palliative Care |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jbUSDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA114 |date=22 September 2016 |publisher=[[Oxford University Press]] |isbn=978-0-19-873372-0 |pages=114– |url-status=live |archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20170908185726/https://books.google.com/books?id=jbUSDQAAQBAJ&pg=PA114 |archivedate=8 September 2017 }}</ref><ref name=Zhang2018 /> |
| <ref name=Zhang2018><pubmed> 30513009</pubmed> </ref> | | | protein_bound = 12–47% (low)<ref name="Kintz2014" /><ref name="sinner" /><ref name="DowdJohnson2016" /> |
| * [[Oral administration|By mouth]]: 16–29%<ref name="Kintz2014" /><ref name="DickmanSchneider2016">'''Andrew Dickman & Jennifer Schneider. (2016).'''<br>The Syringe Driver: Continuous Subcutaneous Infusions in Palliative Care<br>Oxford University Press, pp. 114-</ref><ref name=Zhang2018 /> | |
| | protein_bound = 12–47% (low)<ref name="Kintz2014" /><ref name="sinner" /><ref name="DowdJohnson2016">'''Frank J. Dowd, Bart Johnson & Angelo Mariotti. (2016).'''<br>Pharmacology and Therapeutics for Dentistry – E-Book<br>Elsevier Health Sciences, pp235–</ref> | |
| | metabolism = [[Liver]] ([[demethylation|''N''-demethylation]]):<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref><pubmed>12065445</pubmed></ref> | | | metabolism = [[Liver]] ([[demethylation|''N''-demethylation]]):<ref name="MathewZarate2016" /><ref><pubmed>12065445</pubmed></ref> |
| * Major: [[CYP3A4]] | | * Major: [[CYP3A4]] |
| 61行目: |
49行目: |
| | onset = | | | onset = |
| * Intravenous: seconds<ref name="sinner" /> | | * Intravenous: seconds<ref name="sinner" /> |
| * Intramuscular: 1–5 min<ref name="sinner" /><ref name="Quibell2011">{{cite journal |last1= Quibell |first1= R |last2= Prommer |first2= EE |last3= Mihalyo |first3= M |last4= Twycross |first4= R |last5= Wilcock |first5= A |displayauthors= 4 |title= Ketamine* |journal= [[Journal of Pain and Symptom Management]] |date= March 2011 |volume= 41 |issue= 3 |pages= 640–9 |doi= 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2011.01.001 |pmid= 21419322 |url= http://www.jpsmjournal.com/article/S0885-3924%2811%2900046-7/fulltext |type= Therapeutic Review|doi-access= free }}</ref> | | * Intramuscular: 1–5 min<ref name="sinner" /><ref name="Quibell2011" /> |
| * Subcutaneous: 15–30 min<ref name="Quibell2011" /> | | * Subcutaneous: 15–30 min<ref name="Quibell2011" /> |
| * Insufflation: 5–10 min<ref name="sinner" /> | | * Insufflation: 5–10 min<ref name="sinner" /> |
| 67行目: |
55行目: |
| | elimination_half-life = | | | elimination_half-life = |
| * Ketamine: 2.5–3 hours<ref name="sinner" /><ref name="MathewZarate2016" /> | | * Ketamine: 2.5–3 hours<ref name="sinner" /><ref name="MathewZarate2016" /> |
| * Norketamine: 12 hours<ref name="Quibell2011" ><pubmed> 21419322</pubmed></ref> | | * Norketamine: 12 hours<ref name="Quibell2011" /> |
| | duration_of_action = | | | duration_of_action = |
| * Intramuscular: 0.5–2 hours<ref name="Quibell2011" /> | | * Intramuscular: 0.5–2 hours<ref name="Quibell2011" /> |
| 99行目: |
87行目: |
| | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} | | | ChEMBL_Ref = {{ebicite|correct|EBI}} |
| | ChEMBL = 742 | | | ChEMBL = 742 |
| | synonyms = CI-581; CL-369; CM-52372-2<ref name="MortonHall2012">'''I.K. Morton, & Judith M. Hall. (2012).'''<br>Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms<br>Springer Science & Business Media, pp159–</ref> | | | synonyms = CI-581; CL-369; CM-52372-2<ref name="MortonHall2012" /> |
|
| |
|
| <!--Chemical data--> | | <!--Chemical data--> |
| 120行目: |
108行目: |
| | alt=|caption=|type=|MedlinePlus=|licence_EU=|pregnancy_category= | | | alt=|caption=|type=|MedlinePlus=|licence_EU=|pregnancy_category= |
| }} | | }} |
|
| |
| == 歴史 ==
| |
| 1962年に米国[[w:Parke-Davis|パーク・デービス社]]によって、[[麻酔薬]][[フェンサイクリジン]]([[phencyclidine]], PCP)の代用物(半減期が短い化合物)として、[[CI-581]](後のケタミン)が合成された。1964年、[[w:University of Michigan|ミシガン大学]]のEdward F. Domino博士らが、健常者(囚人)を対象とした実験を実施した<ref name=Domino1965><pubmed>14296024</pubmed></ref> 。ケタミンもPCP同様、[[中枢神経系]]の抑制作用、[[鎮痛]]作用が見られた。一方、呼吸抑制が少なく、血圧低下も招きにくいことから、ケタミンは[[大脳皮質]]は抑制しても、いわゆる[[大脳辺縁系]]は抑制しないと考えられ、[[解離性麻酔薬]](dissociative anesthetic)と命名された<ref name=Domino1965><pubmed>14296024</pubmed></ref><ref name=Domino2010><pubmed>20693870</pubmed></ref> 。
| |
|
| |
| ケタミンは、他の麻酔薬と比べて、呼吸抑制などの副作用が低いため、[[wj:世界保健機関|世界保健機関]]による[[wj:必須医薬品|必須医薬品]]になっており、麻酔薬として世界中で使用されている。しかし、ケタミンは、[[悪夢]]、[[浮遊感覚]]([[幽体離脱]])などの[[解離症状]]や[[幻覚]]などの精神病症状も引き起こし、1970年代後半から米国の若者の間でその乱用が大きな社会問題になり、わが国でも2007年に麻薬指定された。
| |
|
| |
| == 薬理作用 ==
| |
| ケタミンの麻酔・鎮痛作用および上記の副作用(解離症状、精神病症状)は、グルタミン酸受容体の一つであるNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体の拮抗作用によると考えられている<ref name=Domino2010><pubmed>20693870</pubmed></ref>。NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体拮抗薬のヒトにおける精神病惹起作用は、[[NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体]]遮断作用の強さに比例しているため、[[統合失調症]]の[[グルタミン酸仮説(統合失調症)|NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体機能低下仮説]]が提唱されている<ref name=Javitt1991><pubmed>1654746</pubmed></ref>。またケタミンは、[[オピオイド受容体]]、[[シグマ受容体]]などにも弱い親和性を有する<ref name=Domino2010><pubmed>20693870</pubmed></ref>。
| |
|
| |
| ケタミンは[[wj:不斉炭素|不斉炭素]]を有するため、二つの[[wj:光学異性体|光学異性体]]を有する。NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体への親和性は、[[ケタミン|(S)-ケタミン]]の方が[[ケタミン|(R)-ケタミン]]より3-4倍程度強いことが知られており<ref name=Domino2010><pubmed>20693870</pubmed></ref>、ヨーロッパや中国では(S)-ケタミンは麻酔薬(麻酔作用は、NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体遮断作用が関与)として使用されている。一方、米国や日本では、(S)-ケタミンは麻酔薬として認可されていない。
| |
|
| |
| == 代謝 ==
| |
| ケタミンは肝臓の[[wj:チトクロームP450|チトクロームP450]]により[[ノルケタミン]]、[[ヒドロキシノルケタミン]]、[[デヒドロノルケタミン]]などに代謝される。ノルケタミンがケタミンの主代謝物である。
| |
|
| |
| ==適用==
| |
| ===麻酔薬===
| |
| 麻酔薬として[[wj:静脈投与|静脈投与]]量と[[wj:筋肉注射|筋肉注射]]用がある<ref name=公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会2015>'''公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会(2015)'''<br>麻酔薬および麻酔関連薬使用ガイドライン 第3版 第4訂 [https://anesth.or.jp/files/pdf/venous_medicine_20190905.pdf| PDF]</ref>。静注としては、[[アトロピン]]の前投与後、初回体重あたり1-2 mg/kgを緩徐(1分間以上)に静注し、必要に応じて初回量と同じ量又は半量を追加する。例えば、成人に静注した場合、0.5 ~1分で手術可能な麻酔状態が得られ、麻酔作用は5~10分前後持続する。静注用ケタミンの重大な副作用は、[[wj:急性心不全|急性心不全]](頻度不明)、呼吸抑制(2.5%)、無呼吸(頻度不明)、舌根沈下(頻度不明)、[[痙攣]](0.4%)、覚醒時反応(悪夢、浮遊感覚などの解離症状や幻覚あるいは興奮、錯乱状態など)などがある。その他の副作用(1.5%以上)に、[[頭痛]]、[[夢]]、[[wj:発疹|発疹]]、[[悪心]]・[[嘔吐]]、[[食思不振]]、[[発熱]]、[[発汗]]、[[悪寒]]などがある。
| |
|
| |
| 筋注としては、アトロピンの前投与後、初回体重あたり5-10 mg/kgを筋注し、必要に応じて初回量と同じ量又は半量を追加する。例えば、成人及び小児に筋注した場合、3~4分で手術可能な麻酔状態が得られ、麻酔作用は12~25分前後持続する。筋注用ケタミンの重大な副作用は、静注用ケタミンと同様である。
| |
|
| |
| ケタミンは、獣医学領域で幅広く使用されている。他の麻酔薬と比較して安全域が広く、多様な動物種(小型から大型動物)に使用でき、1回投与で確実な鎮静化・不動化が出来る特徴がある。筋肉内投与が可能な麻酔薬は他にないので、筋注用ケタミンは、動物の麻酔薬としてよく使用されている。
| |
|
| |
| 強い鎮痛作用、麻酔作用がある一方、呼吸抑制は見られたとしても一過性のことが多く、直接血圧低下を起こすことが少ないことなどから、全身麻酔および吸入麻酔の補助などに用いられている。筋弛緩作用はなく、むしろ筋緊張が亢進することがある<ref name=公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会2015></ref>。
| |
|
| |
| 麻酔から覚醒する際に、幻覚、悪夢、浮遊感覚などの症状が観察される。
| |
|
| |
| === 抗うつ作用 ===
| |
| 1970年代後半から1980年代初頭に、米国ではPCPやケタミンの乱用が大きな社会問題になった。これらの薬物乱用者の中にはうつ症状を呈する者も多く、一部には、既存の[[抗うつ薬|モノアミン系抗うつ薬]]に効果が無く、即効性抗うつ効果を期待してケタミンを使用する者もいたという<ref name=Domino2010><pubmed>20693870</pubmed></ref>。このように、一部の医師や研究者は、ケタミンの抗うつ効果に気づいていたが、精神病惹起作用を有する乱用薬物ケタミンが抗うつ薬になるとは思っていたなかったとEdward F. Domino博士は後に語っている。
| |
|
| |
| 2000年にYale大学のJohn H. Krystal博士らは、うつ病患者を対象とした[[wj:二重盲検試験|プラセボ対照二重盲検試験]]を実施し、ケタミンの抗うつ効果を科学的に証明した<ref name=Berman2000><pubmed>10686270</pubmed></ref> 。ケタミン投与後、精神病惹起作用や解離症状が出現し、1時間以内に消失した。その後、抗うつ効果がみられ、投与3日後でも確認された<ref name=Berman2000><pubmed>10686270</pubmed></ref> 。当初、この論文は注目されなかったが、2006年に[[w:National Institute of Mental Health|米国精神衛生研究所]](NIH/NIMH)のCarlos A. Zarate博士らが、治療抵抗性うつ病患者を対象としたプラセボ対照二重盲検試験を実施し、ケタミンの即効性抗うつ効果と持続(1週間以上)効果を報告した<ref name=Zarate2006><pubmed>16894061</pubmed></ref> 。興味深いことに、ケタミンは重度のうつ病患者の希死念慮・自殺願望にも即効性の効果がある事が報告された<ref name=Grunebaum2018><pubmed>29202655</pubmed></ref> 。その後、多くの研究グループの追試によりケタミンの抗うつ効果および希死念慮抑制効果が確認された<ref name=Newport2015><pubmed>26423481</pubmed></ref><ref name=Kishimoto2016><pubmed>26867988</pubmed></ref><ref name=Wilkinson2018><pubmed>28969441</pubmed></ref> 。欧米では、ケタミンの抗うつ効果は、気分障害研究の歴史において、過去60年間で最も大きな発見、あるいは精神医学分野では[[クロルプロマジン]]以来の大発見と言われている<ref name=橋本謙二2020a>'''橋本謙二(2020)'''<br>難治性うつ病治療に対するケタミンへの期待<br>医学のあゆみ 272(5):495-499</ref><ref name=橋本謙二2020b>'''橋本謙二(2020)'''<br>難治性うつ病の画期的治療薬として期待されるケタミン<br>精神神経学雑誌 122(6):473-480</ref> 。しかしながら、ケタミンの問題点(投与直後の精神病惹起作用、解離症状、繰り返し投与による薬物依存など)が解決していないにも関わらず、米国のケタミンクリニックや病院では、難治性うつ病に対してケタミンの適応外使用が日常的に行われている<ref name=Sanacora2017><pubmed>28249076</pubmed></ref> 。
| |
|
| |
| ==== 抗うつ作用におけるNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体の役割 ====
| |
|
| |
| ケタミンの主の薬理作用は、グルタミン酸受容体の一つであるNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体の拮抗作用であることから、多くの研究者はケタミンの抗うつ作用はNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体の拮抗作用と信じており、海外の幾つかの製薬企業がNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体拮抗薬を開発した。しかしながら、ケタミン以外のNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体拮抗薬は、うつ病患者においてケタミン様の強力は抗うつ効果を示さず、開発中止に追い込まれた<ref name=Hashimoto2019><pubmed>31215725</pubmed></ref><ref name=Hashimoto2020a><pubmed>32224141</pubmed></ref><ref name=Yang2019><pubmed>31699965</pubmed></ref>。興味深い事に、強力で選択性の高いNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体[[拮抗薬]][[(+)-MK-801]] (dizocilpine)は、うつ病患者において抗うつ効果を示さなかった<ref name=Hashimoto2020a><pubmed>32224141</pubmed></ref>。さらに、これまで実施されたケタミンの臨床試験結果から、ケタミン投与後の解離症状は、ケタミンの抗うつ効果には関連ないことが判ってきた。以上の事から、Hashimotoらはケタミンの抗うつ効果におけるNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体拮抗作用以外の関与を考える必要性を提唱した<ref name=Hashimoto2019><pubmed>31215725</pubmed></ref><ref name=Hashimoto2020b><pubmed>32430328</pubmed></ref><ref name=Hashimoto2020a><pubmed>32224141</pubmed></ref><ref name=Yang2019><pubmed>31699965</pubmed></ref><ref name=橋本謙二2020c>'''橋本謙二 (2020)'''<br>NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体はケタミンの抗うつ効果に関係しているか?<br>臨床精神薬理 23, 787-792.</ref>。
| |
|
| |
| ==== (S)-ケタミン ====
| |
| esketamine
| |
|
| |
| 米国[[wj:ジョンソン・エンド・ジョンソン|Johnson & Johnson社]]は、NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体への親和性が強い(S)-ケタミンの鼻腔内投与を難治性うつ病患者の追加投与として開発した。2016年に治療抵抗性うつ病患者に対する(S)-ケタミン(0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg)の静脈投与によるプラセボ対照二重盲検試験が報告された。(S)-ケタミンは即効性抗うつ効果を示したが、副作用も多かった<ref name=Singh2016><pubmed>26707087</pubmed></ref>。その後、Johnson & Johnson社は、(S)-ケタミンの鼻腔内投与を難治性うつ病患者の追加投与として開発し、2019年に米国およびヨーロッパで承認された<ref name=Jauhar2019><pubmed>31548292</pubmed></ref><ref name=Kim2019><pubmed>31116916</pubmed></ref>。しかしながら、副作用の問題から、(S)-ケタミンはリスク評価軽減戦略(Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies, REMS)の下で使用しなければならず、患者は点鼻薬を医師の診察室や医療機関において、自分で投与できるが、自宅に持って帰ることは禁止されている<ref name=橋本謙二2020b></ref> 。さらに(S)-ケタミンの抗うつ効果に関する問題点も指摘されている<ref name=Horowitz2020><pubmed>32456714</pubmed></ref><ref name=Turner2019><pubmed>31680014</pubmed></ref>。
| |
|
| |
| ==== (R)-ケタミン ====
| |
| arketamine
| |
|
| |
| ケタミンの抗うつ作用にはNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体遮断作用は重要でないと考えたHashimotoらは、うつ病の動物モデルを用いて、二つの光学異性体を比較し、(R)-ケタミンが、(S)-ケタミンよりも抗うつ効果が強く、持続効果も長いことを報告した<ref name=Yang2015><pubmed>26327690</pubmed></ref><ref name=Zhang2014><pubmed>24316345</pubmed></ref>。これらの論文はほとんど注目されなかったが、後に、米国[[wj:メリーランド大学|メリーランド大学]]や[[wj:米国衛生研究所|米国衛生研究所]](NIH)のグループの追試により注目され<ref name=Zanos2016><pubmed>27144355</pubmed></ref>、以後、多くの研究者が(R)-ケタミンの抗うつ効果に注目するようになった。両異性体の薬物動態には大きな差が無いことから、両異性体の抗うつ効果の差は、薬物動態の寄与は低いと考えられた。NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体への親和性は、(S)-ケタミンの方が(R)-ケタミンより3-4倍程度強いことから、ケタミンの抗うつ作用には、NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体以外の作用が関与する可能性が指摘されている<ref name=Hashimoto2019><pubmed>31215725</pubmed></ref><ref name=Hashimoto2020b><pubmed>32430328</pubmed></ref><ref name=Hashimoto2020a><pubmed>32224141</pubmed></ref><ref name=Yang2019><pubmed>31699965</pubmed></ref><ref name=橋本謙二2020c />。
| |
|
| |
| 2020年にブラジルの研究者が、治療抵抗性うつ病患者を対象とした(R)-ケタミン(0.5 mg/kg)のオープンラベルの予備試験を報告した。(R)-ケタミンは、静脈投与1時間後には強力な抗うつ効果を示し、1週間後でも確認された。興味深い事に、(R)-ケタミンの投与量は、上記の(S)-ケタミンの投与量(0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg)<ref name=Singh2016><pubmed>26707087</pubmed></ref>より高いにも関わらず、解離症状などの副作用は殆ど観察されなかった<ref name=Leal2020><pubmed>32078034</pubmed></ref>。(R)-ケタミンの即効性抗うつ効果と副作用については、今後、大規模な臨床試験が必要であろう。
| |
|
| |
| ====抗うつ作用の機序 ====
| |
| =====mechanistic target of rapamycin系 =====
| |
| 2010年に米国[[wj:Yale大学|Yale大学]]の[[w:Ronald S. Duman|Ronald S. Duman]]博士らは、ケタミンの抗うつ作用に細胞内[[mechanistic target of rapamycin]] ([[mTOR]])系が関与している事を報告した<ref name=Li2010><pubmed> 20724638 </pubmed></ref>。一方、ケタミンの抗うつ作用にmTOR系が関与しないという反論も報告された<ref name=Zanos2016><pubmed>27144355</pubmed></ref><ref name=Autry2011><pubmed>21677641</pubmed></ref> 。Hashimotoらのグループは、mTOR系は(S)-ケタミンの抗うつ作用には関与するが、(R)-ケタミンの抗うつ作用には関与しないことを報告した<ref name=Yang2018><pubmed>28651788</pubmed></ref> 。2020年に、Dumanらは、mTORの阻害薬[[ラパマイシン]]が、治療抵抗性うつ病患者に対するケタミンの抗うつ効果をブロックせず、逆に増強することを発表した<ref name=Abdallah2020a><pubmed>32092760</pubmed></ref>。ケタミンの抗うつ作用におけるmTOR系の役割については、今後詳細に検討する必要がある。
| |
|
| |
| ===== 脳由来神経栄養因子 =====
| |
| 2011年に、米国Southwestern大学の[[w:Lisa Monteggia|Lisa M. Monteggia]]博士(現:[[ヴァンダービルト大学|Vanderbilt University]])らは、ケタミンの抗うつ効果には、[[脳由来神経栄養因子]]([[brain-derived neurotrophic factor]], [[BDNF]])が関与していることを報告した<ref name=Autry2011><pubmed>21677641</pubmed></ref>。Hashimotoらのグループも、二つのケタミン異性体の抗うつ効果は、[[TrkB受容体]]拮抗薬でブロックされることから、BDNF-TrkB系が重要であることを報告した<ref name=Yang2015><pubmed>26327690</pubmed></ref>。ケタミンの抗うつ作用におけるBDNF-TrkB系の役割は、多くの研究グル-プから追試されており、ケタミンの持続効果(1週間以上持続)に関与していると推測されている。
| |
|
| |
| ===== トランスフォーミング成長因子 =====
| |
| 2020年に、Hashimotoらのグループは、[[RNA-seq]]解析を用いて、ケタミン異性体の抗うつ効果の差に、[[トランスフォーミング成長因子β1]] ([[TGF-β1]])が関与していること<ref name=Zhang2020><pubmed>32066676</pubmed></ref> 、およびTGF-β1がうつ病モデルにおいて即効性抗うつ効果と持続効果を有することを報告した<ref name=Zhang2020><pubmed>32066676</pubmed></ref> 。
| |
|
| |
| ===== 代謝物(2R,6R)-ヒドロキシノルケタミン、その他 =====
| |
| 2016年に米国Maryland大学と米国衛生研究所のグループが、ケタミンの抗うつ効果は、ケタミン自体でなく、(R)-ケタミンから代謝される[[(2R,6R)-ヒドロキシノルケタミン]]([[hydroxynorketamine]], HNK)であるとNature誌に報告した<ref name=Zanos2016><pubmed>27144355</pubmed></ref>。(2R,6R)-HNKは(R)-ケタミンの主代謝物ではないが、この論文では、ケタミンと同じ投与量(10 mg/kg)で抗うつ効果を確認している<ref name=Zanos2016><pubmed>27144355</pubmed></ref>。一方、Hashimotoらのグループは、(2R,6R)-HNKの生成はケタミンの抗うつ効果には必須でないと報告した<ref name=Chang2018><pubmed>29893929</pubmed></ref><ref name=Shirayama2018><pubmed>29155993</pubmed></ref><ref name=Yamaguchi2018><pubmed>29802366</pubmed></ref><ref name=Yang2017><pubmed>28104224</pubmed></ref><ref name=Zhang2018a><pubmed>29997397</pubmed></ref><ref name=Zhang2018b><pubmed>30215218</pubmed></ref>。
| |
|
| |
| 2019年に、米国Maryland大学と米国衛生研究所のグループは、(2R,6R)-HNKの生成は(R)-ケタミンの作用に一部関与しているかもしれないとした<ref name=Zanos2019><pubmed>30941749</pubmed></ref> 。一方、同グループは2020年に、治療抵抗性うつ病患者を対象とした臨床試験において、ケタミンの抗うつ効果と血液中(2R,6R)-HNK濃度との間には負の相関があるという、(2R,6R)-HNKがケタミンの抗うつ作用に関与するという仮説とは逆の結果が報告され<ref name=Farmer2020><pubmed>32252062</pubmed></ref>、抗うつ薬としての(2R,6R)-HNKの開発に対して疑問も提起されている<ref name=Abdallah2020><pubmed>32291407</pubmed></ref>。米国衛生研究所のCarlos Zarate博士らが、(2R,6R)-HNKの臨床試験を計画しているという<ref name=Hashimoto2019><pubmed>31215725</pubmed></ref>。
| |
|
| |
| なお、[[マウス]]を用いた[[強制水泳試験]]や[[尾懸垂試験]]は、うつ病患者の抗うつ効果を必ずしも予測しないので、注意が必要である<ref name=Reardon2019><pubmed>31337906</pubmed></ref>。現時点でケタミンやケタミン異性体の抗うつ効果の詳細な作用機序は明らかでないが、将来、ケタミンの新規治療ターゲットが同定されれば、ケタミンの副作用を有さない新規抗うつ薬の創製につながると期待される。
| |
|
| |
| ==副作用==
| |
| 麻酔薬の箇所で記載したように、静注用および筋注用ケタミンの重大な副作用は、急性心不全(頻度不明)、呼吸抑制(2.5%)、無呼吸(頻度不明)、舌根沈下(頻度不明)、痙攣(0.4%)、覚醒時反応(悪夢、浮遊感覚などの解離症状や幻覚あるいは興奮、錯乱状態など)などがある。また麻酔から覚醒する際に、幻覚、悪夢、浮遊感覚などの症状が観察される。一方、抗うつ作用として使用されるケタミンの投与量(0.5 mg/kg, 40-min infusion)では、麻酔効果は無く、投与後1時間以内に、幻覚、悪夢、浮遊感覚などの症状が観察される。ケタミンの麻酔・鎮痛作用および上記の副作用(精神病惹起作用、解離症状)は、グルタミン酸受容体の一つであるNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体の拮抗作用によると考えられている<ref name=Domino2010></ref>。
| |
|
| |
| ケタミンはうつ病患者において即効性抗うつ作用および希死念慮低下作用を示すが、ケタミンの副作用(精神病惹起作用、解離症状)は臨床応用を考えた場合、解決すべき大きな課題である。精神病惹起作用の指標である運動量亢進作用、[[プレパルス抑制]]障害、[[場所嗜好性試験]]、[[前頭皮質]]における[[パルブアルブミン]]陽性細胞の低下は、(S)-ケタミンの単回投与および繰り返し投与で起きるが、(R)-ケタミンでは起きなかった<ref name=Yang2015><pubmed>26327690</pubmed></ref><ref name=Chang2019><pubmed>31034852</pubmed></ref><ref name=Yang2016><pubmed>27043274</pubmed></ref>。 (S)-ケタミンや(R,S)-ケタミンの投与では、[[ラット]][[脳梁膨大後部皮質]]における[[熱ショックタンパク質]](神経障害マーカー)の誘導が起きるが、(R)-ケタミンの投与では起きなかった<ref name=Tian2018><pubmed>30030125</pubmed></ref> 。[[wj:浜松ホトニクス社|浜松ホトニクス社]]との無麻酔[[サル]][[PET]]を用いた研究から、(R)-ケタミンの静脈投与は、ドパミンD2受容体に影響を与えないが、(S)-ケタミンの静脈投与は[[ドパミン]][[D2受容体]]を有意に低下することを報告した<ref name=Hashimoto2017><pubmed>27091456</pubmed></ref>。この結果は、(S)-ケタミン投与により、[[シナプス前部]]からドパミン放出が起きていることを示しており、ヒトにおける(S)-ケタミン静脈投与後の精神病惹起作用および解離症状<ref name=Singh2016><pubmed>26707087</pubmed></ref>と関連していると思われる。このように、ケタミンの上記の副作用は、主にNMDA型グルタミン酸受容体が関与していることから、NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体への親和性が低い(R)-ケタミンは(R,S)-ケタミンや(S)-ケタミンより副作用の少ない安全な抗うつ薬として期待される<ref name=橋本謙二2020a /><ref name=橋本謙二2020b /> 。
| |
|
| |
| ==研究利用==
| |
| === 統合失調症モデル ===
| |
| 前述の通り、ミシガン大学のEdward F. Domino博士らは、PCPやケタミンをヒトに投与すると統合失調症と酷似した症状が出現することを報告した<ref name=Domino2010><pubmed>20693870</pubmed></ref><ref name=Domino1965><pubmed>14296024</pubmed></ref>が、その後、米国でPCPの乱用が問題になった際、PCP使用者は、統合失調症と酷似した症状を有することから、統合失調症のPCPモデルが提唱された<ref name=Javitt1991><pubmed>1654746</pubmed></ref> 。1994年にイェール大学のJohn H. Krystal博士らは、ケタミンを健常者に投与すると、統合失調症の全ての症状([[陽性症状]]、[[陰性症状]]、[[認知機能障害]])を引き起こすことを報告した<ref name=Krystal1994><pubmed>8122957</pubmed></ref>。米国では、健常者にケタミンを投与して統合失調症様の症状を引き起こし、脳での生化学的変化や候補薬剤(抗精神病薬)の評価に幅広く使用されている。前述したように、ケタミンは治療抵抗性うつ病の治療に適応外使用されているが、うつ病患者の認知機能障害を悪化させず、逆に改善する作用がある。以上の事から、ヒトの認知機能に対するケタミンの作用は、今後、詳細に検討する必要がある。
| |
|
| |
| === 実験動物の手術時の麻酔薬ケタミンの使用 ===
| |
| ケタミンは、実験用動物(マウス、ラット、[[イヌ]]、サルなど)の手術時の麻酔薬として使用される場合も多い。ケタミンの麻酔効果は短期間であるが、別の作用(抗うつ作用を含む様々な作用)はケタミン単回投与後1~2週間以上持続することが、うつ病患者やげっ歯類を用いた研究で数多く報告されている。実験動物の手術時に麻酔薬としてケタミンを使用すると、その後の実験(行動評価、生化学的評価、組織化学的評価など)に影響を与えると予想される。例えば、脳の特定部位の破壊、脳の特定部位へのプローブの挿入、末梢臓器の摘出などの実験の際には、ケタミン麻酔は適していない可能性がある。
| |
|
| |
| == 関連項目==
| |
| * [[うつ病]]
| |
| * [[統合失調症]]
| |
| * [[抗うつ薬]]
| |
| * [[NMDA型グルタミン酸受容体]]
| |
|
| |
| ==外部リンク==
| |
| * [https://anesth.or.jp/files/pdf/venous_medicine_20190905.pdf 麻酔薬および麻酔関連薬使用ガイドライン] 2018 公益社団法人日本麻酔科学会 第3版第4訂
| |
|
| |
| == 参考文献 ==
| |
| <references />
| |