「錯覚」の版間の差分
Akiyoshi Kitaoka (トーク | 投稿記録) 細編集の要約なし |
Akiyoshi Kitaoka (トーク | 投稿記録) 細編集の要約なし |
||
| 1行目: | 1行目: | ||
英:illusion 独:Täuschung 仏:illusion | 英:illusion 独:Täuschung 仏:illusion | ||
錯覚とは、ある対象についての知覚がその対象の真の性質と認識されるものと異なる場合の知覚である。 | 錯覚とは、ある対象についての知覚がその対象の真の性質と認識されるものと異なる場合の知覚である。 | ||
==錯覚とは== | ==錯覚とは== | ||
| 7行目: | 7行目: | ||
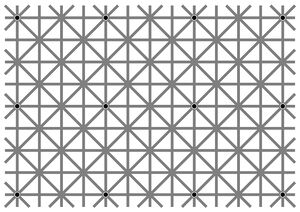
[[ファイル:NinioextinctionillusionL.jpg|サムネイル|図1 ニニオ・スティーブンスの消失錯視(Ninio-Stevens' extinction illusion)<ref>Ninio, J. & Stevens, K. A. (2000). Variations on the Hermann grid: an extnction illusion. Perception, 29, 1209-1217.</ref>。垂直線・水平線の交点12箇所に黒いドットが描かれているが、周辺視では消えて見える。]] | [[ファイル:NinioextinctionillusionL.jpg|サムネイル|図1 ニニオ・スティーブンスの消失錯視(Ninio-Stevens' extinction illusion)<ref>Ninio, J. & Stevens, K. A. (2000). Variations on the Hermann grid: an extnction illusion. Perception, 29, 1209-1217.</ref>。垂直線・水平線の交点12箇所に黒いドットが描かれているが、周辺視では消えて見える。]] | ||
知覚的錯覚は、その感覚の種類に応じて、錯視、錯聴、錯触などに区別できる。視覚の錯覚である錯視は、視覚のモダリティに対応して、幾何学的錯視(大きさの錯視、傾きの錯視、位置の錯視)、明るさや色の錯視、運動視の錯視などに分類できる。聴覚の錯覚である錯聴には、連続聴効果(auditory continuity illusion)<ref>Miller, G. A., & Licklider, J. C. R. (1950). The intelligibility of interrupted speech. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 22,167-173.</ref><ref>Warren, R. M., Wrightson, J. M., & Puretz, J. (1988). Illusory continuity of tonal and infratonal periodic sounds. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 84, 1338-1342.</ref> | 知覚的錯覚は、その感覚の種類に応じて、錯視、錯聴、錯触などに区別できる。視覚の錯覚である錯視は、視覚のモダリティに対応して、幾何学的錯視(大きさの錯視、傾きの錯視、位置の錯視)、明るさや色の錯視、運動視の錯視などに分類できる。聴覚の錯覚である錯聴には、連続聴効果(auditory continuity illusion)<ref>Miller, G. A., & Licklider, J. C. R. (1950). The intelligibility of interrupted speech. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 22,167-173.</ref><ref>Warren, R. M., Wrightson, J. M., & Puretz, J. (1988). Illusory continuity of tonal and infratonal periodic sounds. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 84, 1338-1342.</ref>などが知られる。触覚の錯覚である錯触には、ベルベットハンド錯覚(velvet hand illusion)<ref>Mochiyama, H., Sano, A., Takesue, N., Kikuuwe, R., Fujita, K., Fukuda, S., Marui, K., & Fujimoto, H. (2005). Haptic illusions induced by moving line stimuli. Proc. World Haptic Conference,645–648.</ref>や がある。ファントムセンセーションなどがある。温度感覚の錯覚としては、がある。アリストテレスの錯覚 ラバーハンド錯覚 多感覚の相互作用における錯覚もある。たとえば、腹話術効果は、視覚の情報が優位となって引き起こされる聴覚の錯覚である。シャルパンテイエ効果は、視覚の情報が優位となって引き起こされる重さの知覚の錯覚である。サーマルグリル錯覚(thermal grill illusion)は、温度感覚が痛覚を引き起こす例である<ref>Craig, A. D., & Bushnell, M. C. (1994). The thermal grill illusion: Unmasking the burn of cold pain. Science, 265 (5169), 252–255.</ref>。 | ||
認知的錯覚には、透明性の錯覚(illusion of transparency)<ref>自分の心の中が他者に読まれているという錯覚で、それを妄想ほど強く確信しているわけではない状態を指す。 Gilovich, T., Savitsky, K., & Medvec, V. H. (1998). The illusion of transparency: Biased assessments of others' ability to read one's emotional states. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(2), 332–346.</ref> 確証バイアス などがある。 | |||
その他、だまし絵(trompe l'oeil)やバーチャルリアリティ(virtual reality)は、知覚的錯覚の応用物と言える。 | その他、だまし絵(trompe l'oeil)やバーチャルリアリティ(virtual reality)は、知覚的錯覚の応用物と言える。 | ||
2023年4月1日 (土) 14:46時点における版
英:illusion 独:Täuschung 仏:illusion
錯覚とは、ある対象についての知覚がその対象の真の性質と認識されるものと異なる場合の知覚である。
錯覚とは
錯覚とは、ある対象についての知覚がその対象の真の性質と認識されるものと異なる場合の知覚である。すなわち、知覚が刺激の客観的性質と一致しない現象を指す[1]。何を知覚するかに応じて、物理的錯覚、知覚的錯覚、認知的錯覚に大別することができる。物理的錯覚とは、知覚を歪める原因が物理現象にある錯覚のことで、蜃気楼やドップラー効果が挙げられる。知覚的錯覚は、感覚・知覚レベルに原因がある錯覚である。視覚性の錯覚は錯視(さくし)と呼ばれ、聴覚性の錯覚は錯聴(さくちょう)と呼ばれる。認知的錯覚とは、思い違い、勘違い、記憶違い、誤解のことである。概して、物理的錯覚と知覚的錯覚は非可逆的(対象についての正しい知識を得ても修正は困難である)で、認知的錯覚は可逆的である(正しい知識を得ることで修正が可能である)。さらに、残像や順応といった現象あるいは機能を、生理的錯覚として知覚的錯覚から独立させる考え方もある[2][3]。
知覚的錯覚は、その感覚の種類に応じて、錯視、錯聴、錯触などに区別できる。視覚の錯覚である錯視は、視覚のモダリティに対応して、幾何学的錯視(大きさの錯視、傾きの錯視、位置の錯視)、明るさや色の錯視、運動視の錯視などに分類できる。聴覚の錯覚である錯聴には、連続聴効果(auditory continuity illusion)[5][6]などが知られる。触覚の錯覚である錯触には、ベルベットハンド錯覚(velvet hand illusion)[7]や がある。ファントムセンセーションなどがある。温度感覚の錯覚としては、がある。アリストテレスの錯覚 ラバーハンド錯覚 多感覚の相互作用における錯覚もある。たとえば、腹話術効果は、視覚の情報が優位となって引き起こされる聴覚の錯覚である。シャルパンテイエ効果は、視覚の情報が優位となって引き起こされる重さの知覚の錯覚である。サーマルグリル錯覚(thermal grill illusion)は、温度感覚が痛覚を引き起こす例である[8]。
認知的錯覚には、透明性の錯覚(illusion of transparency)[9] 確証バイアス などがある。
その他、だまし絵(trompe l'oeil)やバーチャルリアリティ(virtual reality)は、知覚的錯覚の応用物と言える。
幻覚と妄想
錯覚に類似した概念に、幻覚(hallucination)がある。広辞苑第六版[1]によれば、幻覚は「対象のない知覚」である。より明確に錯覚との違いを記述すると、幻覚は外部に対象が存在しない状態で起こる病的な知覚であり、錯覚は外部の対象を刺激として引き起こされる健常な知覚である。ただし、「対象のない知覚」ではあるが、幻覚ではなく錯覚とされる現象もある。一例として、主観的輪郭(subjective contour)[10]がある。それらを引き起こす文脈刺激は周囲に存在することと、現象は病的ではないことから、一般的にはこれらを幻覚には分類しない。その逆に、「対象はあるのに知覚されない」錯覚という現象もある。たとえば、トロクスラー効果(Troxler effect)[11]などの消失錯視群(extinction illusions)(図1)である。それらも、現象は病的ではないことから、幻覚の仲間に入れない。
もう一つ、錯覚に類似した概念に、妄想(delusion)がある。広辞苑第六版[1]によれば、妄想とは「根拠のない主観的な想像や信念。統合失調症などの病的原因によって起こり、事実の経験や論理によっては容易に訂正されることがない」とあり、「誇大―」「被害―」「関係―」と具体的症例が列挙されている。妄想は認知的錯覚に類似しているが、妄想は病的であって、訂正が容易ではない(非可逆的である)という点が、認知的錯覚とは異なる。
以上のように、錯覚、幻覚、妄想の三者は学問的には明確に区別できるものであるが、日常用語や一般の辞書類、あるいは科学的研究においても、それらの区別は必ずしも明確ではない。たとえば、研究社 新英和大辞典 第5版[12]によれば、"illusion"は「1 幻覚、幻影、幻(cf. hallucination) 2 幻想、妄想、迷想、迷い、誤解(delusion) 3 〘心理〙錯覚:an optical~ 錯視」となっていて、錯覚、幻覚、妄想は混同されやすい概念であることがわかる。「てんかん症候学の一部としての幻覚・錯覚・妄想の現象論」(Phenomenology of hallucinations, illusions, and delusions as part of seizure semiology)というタイトルの論文[13]では、錯覚とは既視感(déjà vu)や体外離脱体験(out-of-body experience)のことであった。既視感は病的な認知的錯覚として理解できるので、錯覚は健常的なものばかりではないことがわかる。一方、体外離脱体験は幻覚に分類することが妥当のように思える。
試みに、深層学習の旗手 ChatGPT に「錯覚とは何か」について聞いてみた。ChatGPTは、2022年11月にOpenAIがリリースした対話に特化したWebサービスである。情報を広く収集しているAIなのだから、より一般的な見解が得られる可能性がある。回答は以下のとおりであった(2023年1月8日に筆者が英語で質問し、英語で回答されたものを日本語に翻訳)。「錯覚とは、感覚的な体験における誤った認識や誤解のことである。どの感覚にも起こる可能性があるが、最も一般的なのは視覚である。錯覚は、物理的な環境、個人の精神状態、あるいは両者の相互作用など、さまざまな要因によって引き起こされる可能性がある。例えば、目の錯覚は、脳が目から受け取った情報を、実際の物理的な世界のあり方とは異なる方法で解釈したときに起こる。その結果、実際には存在しない形や模様が見えるなど、現実のようでいて現実ではない視覚体験をすることがある。また、聴覚、味覚、触覚などにも錯覚が生じることがある。」 上述の英和辞典が錯覚を病的なものと並列させていたことに比べれば、一見健常的なものとしてまとめている。しかし、「現実のようでいて現実ではない視覚体験」という表現に幻覚や病的なものが反映されている。
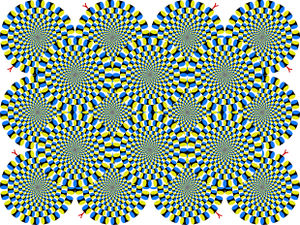
錯覚は、対象についての知識と一致しない知覚(あるいは認知)である。ということは、錯覚は、対象からの刺激によって脳内あるいは心に引き起こされた知覚というだけのものではない。その対象についての「客観的」な知識を事前あるいは事後に持っていて、その知識とその知覚を照合する過程が錯覚の成立に必須である[15]。すなわち、同じ刺激で同じ知覚が得られたとしても、ある人にとっては錯覚であり、別の人には普通の知覚であることがある。たとえば、静止画が動いて見える錯視という現象がある(図2)。ある観察者が図1を見て円盤が回転して見えた時、この画像は静止画ではなく動画であると認識すれば、その観察者にとっては知覚された錯視的運動は錯視ではなく、本物である。この画像が「本当は静止画である」という知識と知覚の不一致を認識して初めて錯視なのである。この錯視的運動が知覚されない観察者にとっては、この図はただの静止画であって錯視画像ではないことは言うまでもないが、それは知覚と知識が一致しているからである。ちなみに、この錯視画像を観察中に運動視を司ると考えられる大脳皮質の領域(hMT+)が活性化される証拠がある[16]。
ヒト以外の動物にも錯視が見えるという報告がある[17][18][19][20]。それによって、ヒトが錯視図形を見て知覚するような「知覚の歪み」が動物にもあるらしい、ということはわかる。しかし、それが動物にとって錯視であるかどうかについては、いくらか疑わしい。たとえばヒトは錯視をおもしろがるが、動物は特段錯視をおもしろがるようには見えない。もちろん、動物が錯視をおもしろがらないからと言って、それが動物が錯視を錯覚として認識していないことの証拠にはならない。しかしながら、「動物にも錯視は見えるか」という問いはヒトと動物の連続性があることを期待して発せられているので、ヒトが錯視をおもしろがるなら動物もおもしろがるはずであるのにそうでないことの説明は必要である[21]。
脳科学辞典は、脳科学分野で研究活動を行っている、または行おうとしている学生と研究者を主に想定し、自分の専門分野から離れた分野の知らない用語の内容をインターネット上で簡単に調べられることを目的としている。本項目の執筆者は錯視の研究者であり、錯視のレビューということであればもう少し具体的に書くこともできたかもしれないが、錯覚といういう広いスタンスの解説ということで、説明が抽象的となってしまった嫌いがある。それならば、少し抽象度を下げて、錯視について調べたい学生と研究者を想定して、彼らに薦めるのに最適な文献を考えてみたい。ところが、実は錯視の指し示す範囲でもまだ広すぎて、選定は容易ではない。2017年に刊行された"The Oxford compendium of visual illusions"という分厚い錯視の専門書[22]があり、世界中の錯視あるいは視覚の研究者が著した書籍であるから、この本を薦めておけばよいのだが、初学者が簡単に錯視を概観するという目的に照らせば、量的に多すぎると言わざるをえない。数十年前であれば、Robinsonの錯視のレビュー本[23]を紹介すれば、手頃な分量であったこともあり、錯視のことを知るにはそれ一冊で十分であったが、今となっては同書は現役の錯視の入門書というよりは、錯視研究史の重要文献である。そこで、ここでは「錯視の科学ハンドブック」[24]、「錯視入門」[25]、"Eye and brain"[4]を、錯視の入門書として挙げておく。認知的錯覚の入門書としては、「錯覚の科学」[5]がある。同じタイトル名に翻訳された"The invisible gorilla"[26]も参考になる。しかし、それらだけでは認知的錯覚を広くカバーできていないので、認知心理学や行動経済学の書籍にも当たって頂きたい。なお、物理的錯覚のまとまった入門書となると、執筆者は寡聞にして推薦できるものを持ち合わせていない。
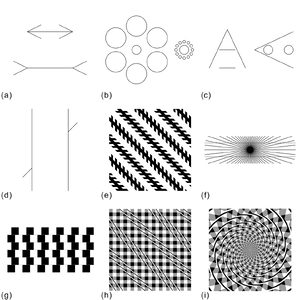
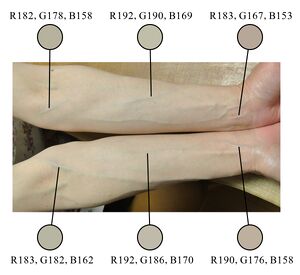
最後に、本項目を読んだ方がすぐにでも活用できるよう、身近な錯視の例をいくつか挙げる。図3は、ミュラー=リヤー錯視をはじめとする古典的な幾何学的錯視の例である。錯視画像の多くは人工的なものであるが、自然に観察できるものもある。例としては、出たばかりの月が大きく見える月の錯視[27](天体錯視とも言う)がある。皆様の手足には、静脈が青く見える錯視が認められる[28][29](図4)。望遠レンズで遠景を撮影すると、奥行き方向の傾斜が急に見える現象(図5)[30]がある。
図5はだまし絵(trompe l'oeil)の一種と考えることができ、だまし絵は錯覚の一種と考えることもできる。しかし、だまし絵については煩雑になるので省略する。奇術(手品)などについても同様である。

- ↑ 新村出(編) (2008). 広辞苑 第六版 岩波書店
- ↑ Gregory, R. L. (1998). Eye and brain: The psychology of seeing. Oxford University Press. (日本語訳:リチャード L. グレゴリー(著)、近藤倫明・中溝幸夫・三浦佳世(訳) (2001). 脳と視覚 ―グレゴリーの視覚心理学― ブレーン出版)
- ↑ 菊池聡 (2020). 放送大学教材 改訂版 錯覚の科学 放送大学教育振興会
- ↑ Ninio, J. & Stevens, K. A. (2000). Variations on the Hermann grid: an extnction illusion. Perception, 29, 1209-1217.
- ↑ Miller, G. A., & Licklider, J. C. R. (1950). The intelligibility of interrupted speech. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 22,167-173.
- ↑ Warren, R. M., Wrightson, J. M., & Puretz, J. (1988). Illusory continuity of tonal and infratonal periodic sounds. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 84, 1338-1342.
- ↑ Mochiyama, H., Sano, A., Takesue, N., Kikuuwe, R., Fujita, K., Fukuda, S., Marui, K., & Fujimoto, H. (2005). Haptic illusions induced by moving line stimuli. Proc. World Haptic Conference,645–648.
- ↑ Craig, A. D., & Bushnell, M. C. (1994). The thermal grill illusion: Unmasking the burn of cold pain. Science, 265 (5169), 252–255.
- ↑ 自分の心の中が他者に読まれているという錯覚で、それを妄想ほど強く確信しているわけではない状態を指す。 Gilovich, T., Savitsky, K., & Medvec, V. H. (1998). The illusion of transparency: Biased assessments of others' ability to read one's emotional states. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75(2), 332–346.
- ↑ Kanizsa, G. (1976). Subjective Contours. Scientific American, 234(4), 48-53.
- ↑ Clarke, F.J.J. (1960). A Study of Troxler's Effect, Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 7(3), 219-236,
- ↑ 小稲義男(編) (1980). 研究社 新英和大辞典 第5版 研究社
- ↑ Kasper, B.S., Kasper, E.M., Pauli, E., & Stefan, H. (2010). Phenomenology of hallucinations, illusions, and delusions as part of seizure semiology. Epilepsy & Behavior, 18, 13-23.
- ↑ Kitaoka, A. (2017). The Fraser-Wilcox illusion and its extension. A. G. Shapiro and D. Todorović (Eds.), The Oxford Compendium of Visual Illusions, Oxford University Press, pp. 500-511.
- ↑ 北岡明佳 (2014). 常識を疑う―錯視は存在するのか? 立命館文學, 636, 24-31.
- ↑ Kuriki, I., Ashida, H., Murakami, I., & Kitaoka, A. (2008). Functional brain imaging of the Rotating Snakes illusion by fMRI. Journal of Vision, 8(10):16, 1-10.
- ↑ Agrillo, C., Parrish, A.E., & Beran, M.J. (2014). Do rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) perceive the Zöllner illusion? Psychonomic Bullutin & Review, 21, 986–994.
- ↑ Bååth, R., Seno, T., & Kitaoka, A. (2014). Cats and illusory motion. Psychology, 5, 1131-1134.
- ↑ Fujita, K., Blough, D.S., & Blough, P.M. (1991). Pigeons see the Ponzo illusion. Animal Learning & Behavior, 19, 283–293.
- ↑ Nakamura, N., Watanabe, S., & Fujita, K. (2008). Pigeons perceive the Ebbinghaus-Titchener circles as an assimilation illusion. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes, 34(3), 375–387.
- ↑ 繁桝算男・北岡明佳 (2018). 連載 人生の智慧のための心理学 第4回 錯覚から世界を考える? 書斎の窓(有斐閣), 655(2018年1月号), 44-48.
- ↑ Shapiro, A. G. & Todorović, D. (Eds.) (2017). The Oxford compendium of visual illusions. Oxford University Press.
- ↑ Robinson, J. O. (1972/1998). The psychology of visual illusion. Mineola, NY: Dover.
- ↑ 後藤倬男・田中平八(編) (2005). 錯視の科学ハンドブック 東京大学出版会
- ↑ 北岡明佳 (2010). 錯視入門 朝倉書店
- ↑ Chabris, C. F. & Simons, D. J. (2010). The invisible gorilla: And other ways our intuitions deceive us. HarperCollins. (日本語訳: クリストファー・チャブリス、ダニエル・シモンズ(著)、木村博江(訳) (2011). 錯覚の科学 文藝春秋)
- ↑ ヘレン・ロス、コーネリス・プラグ(著)、東山篤規(訳) (2014). 月の錯視 なぜ大きく見えるのか 勁草書房
- ↑ Kienle, A., Lilge, L., Vitkin, I. A., Patterson, M. S., Wilson, B. C., Hibst, R., & Steiner, R. (1996). Why do veins appear blue? A new look at an old question. Applied Optics, 35(7), 1151-1160.
- ↑ 北岡明佳 (2019). イラストレイテッド 錯視のしくみ 朝倉書店
- ↑ 北岡明佳 (2020). 現代がわかる心理学 丸善出版