「Transient receptor potentialチャネル」の版間の差分
細 →TRPM |
細 →ファミリー |
||
| (同じ利用者による、間の2版が非表示) | |||
| 4行目: | 4行目: | ||
<font size="+1">[http://researchmap.jp/ymori 森 泰生]</font><br> | <font size="+1">[http://researchmap.jp/ymori 森 泰生]</font><br> | ||
''京都大学大学院工学研究科''<br> | ''京都大学大学院工学研究科''<br> | ||
DOI:<selfdoi /> | DOI:<selfdoi /> 原稿受付日:2018年10月19日 原稿完成日:2018年X月X日<br> | ||
担当編集委員:[http://researchmap.jp/2rikenbsi 林 康紀](京都大学大学院医学研究科システム神経薬理分野)<br> | 担当編集委員:[http://researchmap.jp/2rikenbsi 林 康紀](京都大学大学院医学研究科システム神経薬理分野)<br> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| 30行目: | 30行目: | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Transient receptor potentialチャネルとは == | == Transient receptor potentialチャネルとは == | ||
TRPは、元来、1989年に[[ショウジョウバエ]]の[[光受容]]応答変異株の原因遺伝子として発見された遺伝子名である<ref name=Montell1989><pubmed>2516726</pubmed></ref> 。命名は、trp変異株で[[光受容器電位]](receptor | TRPは、元来、1989年に[[ショウジョウバエ]]の[[光受容]]応答変異株の原因遺伝子として発見された遺伝子名である<ref name=Montell1989><pubmed>2516726</pubmed></ref> 。命名は、trp変異株で[[光受容器電位]](receptor potential)変化が一過性(transient)であることに由来する。TRP遺伝子により構成されるイオンチャネルは多くがNa<sup>+</sup>及び[[カルシウム|Ca<sup>2+</sup>]]の透過性が高い[[陽イオンチャネル]]であるが、Ca<sup>2+</sup>[[イオン選択性フィルター|選択性]]は大きく異なる<ref name=Mulier2017><pubmed>28807146</pubmed></ref> 。 | ||
TRPチャネルは[[ホスファチジルイノシトール|PIP<sub>2</sub>]]、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、[[環状ヌクレオチド]]などの細胞の[[シグナル伝達因子]]や、温度、[[浸透圧]]などの環境因子などに応答することから、物理学的・化学的刺激に対して広い範囲で応答するセンサーとして機能している<ref name=Clapham2003><pubmed>14654832</pubmed></ref> 。TRPチャネルの活性化開口により、[[膜電位]]の変化、Ca<sup>2+</sup>の細胞内流入によるCa<sup>2+</sup>依存性経路の活性化、酵素活性の変化、[[エンドサイトーシス]]・[[エキソサイトーシス]]などの細胞応答が引き起こされる。このため、TRPチャネルは、[[wj:受精|受精]]、[[感覚]]変換、細胞生存、発生など生命の基本的過程において重要な役割を担うことができる<ref name=Sawamura2017>'''Sawamura S, Shirakawa H, Nakagawa T, Mori Y, Kaneko S.'''<br>TRP Channels in the Brain: What Are They There For?.<br>In: Emir TLR, editor. ''Neurobiology of TRP Channels''. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2017. Chapter 16., ''Frontiers in Neuroscience''</ref> 。 | TRPチャネルは[[ホスファチジルイノシトール|PIP<sub>2</sub>]]、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、[[環状ヌクレオチド]]などの細胞の[[シグナル伝達因子]]や、温度、[[浸透圧]]などの環境因子などに応答することから、物理学的・化学的刺激に対して広い範囲で応答するセンサーとして機能している<ref name=Clapham2003><pubmed>14654832</pubmed></ref> 。TRPチャネルの活性化開口により、[[膜電位]]の変化、Ca<sup>2+</sup>の細胞内流入によるCa<sup>2+</sup>依存性経路の活性化、酵素活性の変化、[[エンドサイトーシス]]・[[エキソサイトーシス]]などの細胞応答が引き起こされる。このため、TRPチャネルは、[[wj:受精|受精]]、[[感覚]]変換、細胞生存、発生など生命の基本的過程において重要な役割を担うことができる<ref name=Sawamura2017>'''Sawamura S, Shirakawa H, Nakagawa T, Mori Y, Kaneko S.'''<br>TRP Channels in the Brain: What Are They There For?.<br>In: Emir TLR, editor. ''Neurobiology of TRP Channels''. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2017. Chapter 16., ''Frontiers in Neuroscience''</ref> 。 | ||
| 86行目: | 86行目: | ||
! サブファミリー !! ヒト !! マウス !! 活性化条件 !! 活性化剤 !! 阻害剤 !! 代表的な3次元構造 | ! サブファミリー !! ヒト !! マウス !! 活性化条件 !! 活性化剤 !! 阻害剤 !! 代表的な3次元構造 | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=486&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC1] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc1&search_type=gene&page_num=0 ''TRPC1''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288387 ''Trpc1''] || [[ホスホリパーゼC]](PLC)、ストア枯渇、[[タプシガルジン]]、[[イノシトールトリスリン酸]]([[IP3]])、[[カルバコール]]、[[プロテインキナーゼC]](PKC)、[[プロテインキナーゼA]](PKA)、[[ムスカリン受容体]]、低浸透圧、機械刺激 || [[1-オレオイル-2-アセチルグリセロール]](OAG)、[[テトラヒドロカンナビノール]]、[[一酸化窒素]](NO)、[[カルシウム|Ca<sup>2+</sup>]] | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=486&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC1] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc1&search_type=gene&page_num=0 ''TRPC1''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288387 ''Trpc1''] || [[ホスホリパーゼC]](PLC)、ストア枯渇、[[タプシガルジン]]、[[イノシトールトリスリン酸]]([[IP3]])、[[カルバコール]]、[[プロテインキナーゼC]](PKC)、[[プロテインキナーゼA]](PKA)、[[ムスカリン受容体]]、低浸透圧、機械刺激 || [[1-オレオイル-2-アセチルグリセロール]](OAG)、[[テトラヒドロカンナビノール]]、[[一酸化窒素]](NO)、[[カルシウム|Ca<sup>2+</sup>]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> || La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、[[ジフェニルボリン酸2-アミノエチル]](2-APB)、[[SKF96365]]、[[GsMTx-4]] || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=487&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC2] || 偽遺伝子 || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69134517 ''Trpc2''] || PLC、ストア枯渇 || [[OAG]]、[[2-O,3-O-ジオクタノイル-L-グリセロール]](DOG)、[[1-ステアロイル-2-アラキドニルグリセロール]](SAG)、[[ジアシルグリセロール]](DAG)|| 2-APB、[[U73122]] || | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=487&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC2] || 偽遺伝子 || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69134517 ''Trpc2''] || PLC、ストア枯渇 || [[OAG]]、[[2-O,3-O-ジオクタノイル-L-グリセロール]](DOG)、[[1-ステアロイル-2-アラキドニルグリセロール]](SAG)、[[ジアシルグリセロール]](DAG)|| 2-APB、[[U73122]] || | ||
| 94行目: | 94行目: | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=489&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC4] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc4&search_type=gene ''TRPC4''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/1306 ''Trpc4''] || ストア枯渇、タプシガルジン、IP3、[[ヒスタミン]]、細胞外pH || [[GTPγS]]、La<sup>3+</sup>、NO、[[エングレリンA]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> || La<sup>3+</sup>、[[ニフルミン酸]]、[[4,4'-ジイソチオソアナト-2,2'-スチルベンジスルホン酸二ナトリウム]](DIDS)、[[A-18]]、[[ACC-018]]、[[ML204]]、2-APB、SKF96365|| [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5Z96 5Z96] | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=489&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC4] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc4&search_type=gene ''TRPC4''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/1306 ''Trpc4''] || ストア枯渇、タプシガルジン、IP3、[[ヒスタミン]]、細胞外pH || [[GTPγS]]、La<sup>3+</sup>、NO、[[エングレリンA]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> || La<sup>3+</sup>、[[ニフルミン酸]]、[[4,4'-ジイソチオソアナト-2,2'-スチルベンジスルホン酸二ナトリウム]](DIDS)、[[A-18]]、[[ACC-018]]、[[ML204]]、2-APB、SKF96365|| [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5Z96 5Z96] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=490&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC5] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc5&search_type=gene ''TRPC5''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288399 ''Trpc5''] || PLC、ストア枯渇、[[ATP]]、ヒスタミン、[[PIP5K]]、[[Rac]]、PI3K、[[ミオシン軽鎖キナーゼ]](MLCK)、細胞外pH、機械刺激 || GTPγS、La<sup>3+</sup>、NO、エングレリンA、[[SNAP]]、[[5-nitro-2-PDS]]、過酸化水素(H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>)、Gd<sup>3+</sup> | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=490&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC5] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc5&search_type=gene ''TRPC5''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288399 ''Trpc5''] || PLC、ストア枯渇、[[ATP]]、ヒスタミン、[[PIP5K]]、[[Rac]]、PI3K、[[ミオシン軽鎖キナーゼ]](MLCK)、細胞外pH、機械刺激 || GTPγS、La<sup>3+</sup>、NO、エングレリンA、[[SNAP]]、[[5-nitro-2-PDS]]、過酸化水素(H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>)、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、Pb<sup>2+</sup>、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、[[ロシグリタゾン]]、[[リゾホスファチジルコリン]]、[[ゲニステイン]]、[[ダイゼイン]] || La<sup>3+</sup>、2-APB、SKF96365、BTP2、KB-R7943、[[プロゲステロン]]、ML204、[[ブロモエノールラクトン]]、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、[[クロルプロマジン]]、[[フルフェナム酸]]、GsMTx-4|| | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=491&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC6] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc6&search_type=gene ''TRPC6''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288405 ''Trpc6''] || ATP、カルバコール、ヒスタミン、メタコリン、[[バソプレシン]]、[[フッ化アルミニウム]]、[[CaMKII]]、[[PIP3]]、機械刺激 || GTPγS、OAG、SAG、DAG、DOG、[[1-ステアロイル-2-リノレオイルグリセロール]](SLG)、[[RHC80267]]、フルフェナム酸、[[アラキドン酸]]、リゾホスファチジルコリン、[[ハイパフォリン]]、[[hyp 9]]、[[20-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸]](20-HETE) || La<sup>3+</sup>、2- | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=491&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC6] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc6&search_type=gene ''TRPC6''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288405 ''Trpc6''] || ATP、カルバコール、ヒスタミン、メタコリン、[[バソプレシン]]、[[フッ化アルミニウム]]、[[CaMKII]]、[[PIP3]]、機械刺激 || GTPγS、OAG、SAG、DAG、DOG、[[1-ステアロイル-2-リノレオイルグリセロール]](SLG)、[[RHC80267]]、フルフェナム酸、[[アラキドン酸]]、リゾホスファチジルコリン、[[ハイパフォリン]]、[[hyp 9]]、[[20-ヒドロキシエイコサテトラエン酸]](20-HETE) || La<sup>3+</sup>、2-APB、SKF96365、Cd<sup>2+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、U73122、[[アミロライド]]、[[SH045]]、細胞外pH、ACAA、GsMTx-4、KB-R7943、[[ML9]] || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5YX9 5YX9] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=492&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC7] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc7&search_type=gene&page_num=0 ''TRPC7''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863263 ''Trpc7''] || PLC、ストア枯渇、ATP、カルバコール、メタコリン、[[anti-IgM]] || GTPγS、OAG、DOG、DAG、RHC80267、[[トリプシン]]、SNAP || La<sup>3+</sup>、2-APB、SKF96365、[[U73122]]、[[W-13]]、アミロライド、SH045 || | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=492&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPC7] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpc7&search_type=gene&page_num=0 ''TRPC7''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863263 ''Trpc7''] || PLC、ストア枯渇、ATP、カルバコール、メタコリン、[[anti-IgM]] || GTPγS、OAG、DOG、DAG、RHC80267、[[トリプシン]]、SNAP || La<sup>3+</sup>、2-APB、SKF96365、[[U73122]]、[[W-13]]、アミロライド、SH045 || | ||
| 102行目: | 102行目: | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=493&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM1] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm1&search_type=gene ''TRPM1''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/71488877 ''Trpm1''] || || [[硫酸プレグネノロン]] || La<sup>3+</sup>、Zn<sup>2+</sup> || | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=493&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM1] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm1&search_type=gene ''TRPM1''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/71488877 ''Trpm1''] || || [[硫酸プレグネノロン]] || La<sup>3+</sup>、Zn<sup>2+</sup> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=494&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM2] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm2&search_type=gene ''TRPM2''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288417 ''Trpm2''] || > | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=494&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM2] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm2&search_type=gene ''TRPM2''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288417 ''Trpm2''] || >36℃、PTP<u>(編集部コメント:何の略?)</u>による[[チロシンリン酸化]]、[[Sir2]]の結合を介する活性化 || [[アデノシン二リン酸リボース]](ADPR)、[[環状アデノシン二リン酸リボース]](cADPR)、[[ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド]](NAD+)、[[ニコチン酸アデニンジヌクレオチドリン酸]](NAADP)、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、NO、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、アラキドン酸、[[O-アセチルアデノシン二リン酸リボース]](OAADPR)、PIP2、[[GEA 3162]]、SNAP || 2-APB、SB750139-B、[[PJ34]]、[[DPQ]]、[[N-(p-アミルシンナモイル)アントラニル酸]]、[[クロトリマゾール]]、[[エコナゾール]]、フルフェナミン酸、[[ミコナゾール]]、Zn<sup>2+</sup>、ACAA、細胞外H<sup>+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6DRK 6DRK] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=495&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM3] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm3&search_type=gene ''TRPM3''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/74431478 ''Trpm3''] || 温度、低浸透圧による細胞膨張、定常活性化 || [[スフィンガニン]]、[[NN-ジメチル-D-エリスロスフィンゴシン]]、スフィンゴシン、[[ニフェジピン]]、[[硫酸エピプレグナノロン]]、硫酸プレグネノロン|| [[TM3E3]](抗体)、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、La<sup>3+</sup>、2-APB、[[ロシグリタゾン]]、細胞外Na<sup>+</sup>、[[メフェナム酸]]、[[トログリタゾン]]、[[ピオグリタゾン]] || | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=495&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM3] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm3&search_type=gene ''TRPM3''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/74431478 ''Trpm3''] || 温度、低浸透圧による細胞膨張、定常活性化 || [[スフィンガニン]]、[[NN-ジメチル-D-エリスロスフィンゴシン]]、スフィンゴシン、[[ニフェジピン]]、[[硫酸エピプレグナノロン]]、硫酸プレグネノロン|| [[TM3E3]](抗体)、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、La<sup>3+</sup>、2-APB、[[ロシグリタゾン]]、細胞外Na<sup>+</sup>、[[メフェナム酸]]、[[トログリタゾン]]、[[ピオグリタゾン]] || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=496&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM4] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm4&search_type=gene ''TRPM4''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863273 ''Trpm4''] || [[脱分極]]、温度、PIP2、膜伸展、PKCによるリン酸化 || [[デカバナジウム酸]]塩、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、ATP、PIK、BTP2 || La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup> | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=496&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM4] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm4&search_type=gene ''TRPM4''] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863273 ''Trpm4''] || [[脱分極]]、温度、PIP2、膜伸展、PKCによるリン酸化 || [[デカバナジウム酸]]塩、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、ATP、PIK、BTP2 || La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、フルフェナミン酸、スペルミン、[[グリベンクラミド]]、[[DIDS]]、[[アデノシン]]、ADP、AMP、ATP、[[9-フェナントレノール]]、MPB-104、クロトリマゾール、[[アデニリル-イミドジホスファート]](AMP-PNP) || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6BQV 6BQV] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=497&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM5] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm5&search_type=gene TRPM5] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288429 ''Trpm5''] || 脱分極、温度、PIP2、IP3 || [[ニコチン]]、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、 || | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=497&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM5] || [http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm5&search_type=gene TRPM5] || [http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288429 ''Trpm5''] || 脱分極、温度、PIP2、IP3 || [[ニコチン]]、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、 || フルフェナミン酸、[[スペルミン]]、細胞外H<sup>+</sup> || | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=498&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM6]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm6&search_type=gene ''TRPM6'']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863283 ''Trpm6'']||[[ERK1]]/[[Erk2|2]]の活性、定常活性化、細胞内Mg<sup>2+</sup>の低下 || 2-APB、細胞外H<sup>+</sup> || | | [http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=498&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM6]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm6&search_type=gene ''TRPM6'']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863283 ''Trpm6'']||[[ERK1]]/[[Erk2|2]]の活性、定常活性化、細胞内Mg<sup>2+</sup>の低下 || 2-APB、細胞外H<sup>+</sup> || ルテニウムレッド、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、Ca<sup>2+</sup>|| | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=499&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM7]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm7&search_type=gene '' TRPM7 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288441 '' Trpm7 '']|| 脱分極、低浸透圧による細胞膨張、機械刺激、PKA、PLC、PIP2、Mg-ヌクレオチド、細胞内のアルカリ化 || 2-APB、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、[[cAMP]]、ATP、細胞外H<sup>+</sup> || La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、[[プトレシン]]、[[スペルミジン]]、スペルミン、[[ネオマイシン]]、[[ポリリジン]]、[[ルテニウムレッド]]、2-APB、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、スフィンゴシン、[[フィンゴリモド]]、[[NS8593]]、[[waixenicin A]]、カルバコール、[[ナファモスタット]] || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5ZX5 5ZX5] | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=499&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPM7]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpm7&search_type=gene '' TRPM7 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69288441 '' Trpm7 '']|| 脱分極、低浸透圧による細胞膨張、機械刺激、PKA、PLC、PIP2、Mg-ヌクレオチド、細胞内のアルカリ化 || 2-APB、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、[[cAMP]]、ATP、細胞外H<sup>+</sup> || La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、[[プトレシン]]、[[スペルミジン]]、スペルミン、[[ネオマイシン]]、[[ポリリジン]]、[[ルテニウムレッド]]、2-APB、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、スフィンゴシン、[[フィンゴリモド]]、[[NS8593]]、[[waixenicin A]]、カルバコール、[[ナファモスタット]] || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5ZX5 5ZX5] | ||
| 122行目: | 122行目: | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=509&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV3]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv3&search_type=gene '' TRPV3 '']||''Trpv3''|| >32-39℃、PLC、脱分極 || アラキドン酸、メントール、[[シンナムアルデヒド]]、[[オレガノ]]、[[クローブ]]、[[タイム]]、2-APB、カンフル、NO、[[バニリン]]、[[オイゲノール]]、[[カルバクロール]]、[[チモール]]、シトラール、[[ファルネシル二リン酸]]、[[カンナビジオール]]、[[テトロヒドロカンバビバリン]]、[[酢酸インセンソール]]、ジフェニルボロン酸無水物、[[6-tert-ブチル-m-クレゾール]]、ジヒドロカルベオール、[[カルベオール]]、[[ボルネオール]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、[[5-nitro-2-PDS]] || ルテニウムレッド、[[ジフェニルテトラヒドロフラン]]、[[イソペンテニル二リン酸]]、aspirin-triggered resolvin D1|| [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6DVW 6DVW] | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=509&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV3]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv3&search_type=gene '' TRPV3 '']||''Trpv3''|| >32-39℃、PLC、脱分極 || アラキドン酸、メントール、[[シンナムアルデヒド]]、[[オレガノ]]、[[クローブ]]、[[タイム]]、2-APB、カンフル、NO、[[バニリン]]、[[オイゲノール]]、[[カルバクロール]]、[[チモール]]、シトラール、[[ファルネシル二リン酸]]、[[カンナビジオール]]、[[テトロヒドロカンバビバリン]]、[[酢酸インセンソール]]、ジフェニルボロン酸無水物、[[6-tert-ブチル-m-クレゾール]]、ジヒドロカルベオール、[[カルベオール]]、[[ボルネオール]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、[[5-nitro-2-PDS]] || ルテニウムレッド、[[ジフェニルテトラヒドロフラン]]、[[イソペンテニル二リン酸]]、aspirin-triggered resolvin D1|| [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6DVW 6DVW] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=510&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV4]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv4&search_type=gene '' TRPV4 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863295 '' Trpv4 '']|| >27-35℃、細胞膨張、PAR2、PKC、SFK、定常活性化、機械刺激 || アナンダミド、[[4α-ホルボールジデカン酸]](PDD)、NO、[[ホルボール12-ミリスタート13-アセタート]](PMA)、2-APB、[[ビスアンドログラホリド]]、[[GSK1016790A]]、[[4α-ホルボールジヘキサン酸]](PDH)、[[5,6-エポキシエイコサトリエン酸]] (5,6-EET)、[[RN1747]]、[[wj:クエン酸|クエン酸]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、5-nitro-2-PDS || ルテニウムレッド、La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、[[GSK2193874]]、[[HC067047]]、[[RN1734]]|| [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6BBJ 6BBJ] | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=510&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV4]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv4&search_type=gene '' TRPV4 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/69863295 '' Trpv4 '']|| >27-35℃、細胞膨張、PAR2、PKC、SFK、定常活性化、機械刺激 || アナンダミド、[[5',6'-EET]]<u>(編集部コメント:すぐ下にある5,6-エポキシエイコサトリエン酸と重複?)</u>、[[4α-ホルボールジデカン酸]](PDD)、NO、[[ホルボール12-ミリスタート13-アセタート]](PMA)、2-APB、[[ビスアンドログラホリド]]、[[GSK1016790A]]、[[4α-ホルボールジヘキサン酸]](PDH)、[[5,6-エポキシエイコサトリエン酸]] (5,6-EET)、[[RN1747]]、[[wj:クエン酸|クエン酸]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、5-nitro-2-PDS || ルテニウムレッド、La<sup>3+</sup>、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、[[GSK2193874]]、[[HC067047]]、[[RN1734]]|| [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6BBJ 6BBJ] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=511&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV5]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv5&search_type=gene '' TRPV5 '']||''Trpv5''|| 定常活性化、PIP2、Klotho || [[17β-エストラジオール]]、[[1,25-ジヒドロキシビタミンD3]] || ルテニウムレッド、エコナゾール、ミコナゾール、Mg<sup>2+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6DMR 6DMR] | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=511&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV5]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv5&search_type=gene '' TRPV5 '']||''Trpv5''|| 定常活性化、PIP2、Klotho || [[17β-エストラジオール]]、[[1,25-ジヒドロキシビタミンD3]] || ルテニウムレッド、エコナゾール、ミコナゾール、Mg<sup>2+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6DMR 6DMR] | ||
| 128行目: | 128行目: | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=512&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV6]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv6&search_type=gene '' TRPV6 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/100144410 '' Trpv6 '']|| 定常活性化 || 2-APB || ルテニウムレッド、Cd<sup>2+</sup>、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、La<sup>3+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6BOB 6BOB] | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=512&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPV6]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpv6&search_type=gene '' TRPV6 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/100144410 '' Trpv6 '']|| 定常活性化 || 2-APB || ルテニウムレッド、Cd<sup>2+</sup>、Mg<sup>2+</sup>、La<sup>3+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/6BOB 6BOB] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=485&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPA1]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpa1&search_type=gene '' TRPA1 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/70230939 '' Trpa1 '']|| <17℃?、[[ | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=485&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPA1]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=trpa1&search_type=gene '' TRPA1 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/70230939 '' Trpa1 '']|| <17℃?、[[ブレジキニン]]<u>(編集部コメント:ブラジキニンでしょうか?)</u>、[[ポリリン酸]]、トリプシン、カルバコール、細胞内アルカリ化 || テトラヒドロカンナビノール、[[マスタードオイル]]、アリシン、[[シンナムアルデヒド]]、メントール、Ca<sup>2+</sup>、[[カフェイン]]、[[4-HNE]]、[[ホルマリン]]、[[次亜塩素酸ナトリウム]]、H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub>、NO、[[15d-プロスタグランジンJ2]](PGJ2)、[[Δ12-PGJ2]]、[[8-イソPGA2]]、カンフル、[[URB597]]、[[オイゲノール]]、[[ギンゲロール]]、[[サリチル酸メチル]]、イシリン、[[PF-4840154]]、[[ジベンゾオキサゼピン]]、[[モルファントリジン]]、[[1'-アセトキシキャビコールアセテート]]、[[クロロベンジリデンマロノニトリル]]、[[クロロピクリン]]、[[ω-クロロアセトフェノン]]、[[NPPB]]、[[ベンゾキノン]]、[[イソベレラール]]、Cu<sup>2+</sup>、[[ブロモアセトン]]、[[オーラノフィン]]、Cd<sup>2+</sup>、[[アルテピリンC]]、[[4-オキソ-ノネナール]]、[[ニトロオレイン酸]]、[[1,6-ヘキサメチレンジイソシアネート]]、[[N-アセチル-ベンゾキノンイミン]]、[[オレオカンタール]]、O3<u>(編集部コメント:オゾンでしょうか?O<sub>3</sub>?)</u>、、[[2-ペンテナール]]、[[アクロレイン]]、[[salirasib]]、[[アポモルヒネ]]、[[アリルイソチオシアネート]]、[[臭化ベンジル]]、[[ニコチン]]、[[チモール]]、[[プロスタグランジンA2]]、[[crotylaldehyde]]、[[イソシアン酸メチル]]、[[フタル酸ブチル]]、[[ドコサヘキサエン酸]]、[[メチルグリオキサール]]、[[アセトアルデヒド]]、フルフェナム酸、[[イソフルラン]]、[[2-ヨードアセトアミド]]、[[ニフルミン酸]]、[[NaHS]]、[[MTSEA]]、[[ヒドロキシ安息香酸メチル]]、Zn<sup>2+</sup>、[[wj:塩化アンモニウム|NH<sub>4</sub>Cl]]、[[1,4-ジヒドロピリジン]]、ブラジキニン、クロトリマゾール、[[WIN55215-2]]、AM1241、5,6-EET、[[ヘポキシリンA3]]、12S-HPETE、[[wj:二酸化炭素|二酸化炭素]]、酢酸、[[wj:プロピオン酸|プロピオン酸]]、[[wj:ギ酸|ギ酸]]、[[wj:乳酸|乳酸]] || [[AP18]]、[[HC-030031]]、メントール、[[CMP1]]、カフェイン、カンフル、ルテニウムレッド、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、ゲンタマイシン、[[レゾルビンD1]]、[[レゾルビンD2]]、A-967079、[[イソペンテニル二リン酸]]、[[TCS 5861528]]、 || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/3J9P 3J9P] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=504&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPP2]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=pkd2&search_type=gene '' PKD2 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/gene/show/18528 '' Pkd2 '']|| 機械刺激(灌流)、過分極、低浸透圧(PKD1と共発現)、細胞内アルカリ化 || Ca<sup>2+</sup> || Cd<sup>2+</sup>、La<sup>3+</sup>、ニフルミン酸、アミロライド、2-APB、SKF96365、Ni<sup>2+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5K47 5K47] | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=504&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPP2]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=pkd2&search_type=gene '' PKD2 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/gene/show/18528 '' Pkd2 '']|| 機械刺激(灌流)、過分極、低浸透圧(PKD1と共発現)、細胞内アルカリ化 || Ca<sup>2+</sup> || Cd<sup>2+</sup>、La<sup>3+</sup>、ニフルミン酸、アミロライド、2-APB、SKF96365、Ni<sup>2+</sup> || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5K47 5K47] | ||
| 140行目: | 140行目: | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=502&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPML2]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=mcoln2&search_type=gene&page_num=0 '' MCOLN2 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/248562 '' Mcoln2 '']|| 定常活性化、細胞外酸性化 || [[PI(3,5)P2]]、[[SF-21]]、[[SF-41]]、[[SF-81]]、[[ML SA1]] || || | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=502&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPML2]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=mcoln2&search_type=gene&page_num=0 '' MCOLN2 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/248562 '' Mcoln2 '']|| 定常活性化、細胞外酸性化 || [[PI(3,5)P2]]、[[SF-21]]、[[SF-41]]、[[SF-81]]、[[ML SA1]] || || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=503&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPML3]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=mcoln3&search_type=gene&page_num=0 '' MCOLN3 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/75934924 '' Mcoln3 '']|| 定常活性化 || PI(3,5)P2、ML SA1、SF-21、SF-11、[[SF-1]]、[[SF-2]]、[[MK6-83]]、 || ベラパミル、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、細胞外酸性化、Na | |[http://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/ObjectDisplayForward?objectId=503&familyId=78&familyType=IC TRPML3]||[http://human.brain-map.org/microarray/search/show?exact_match=false&search_term=mcoln3&search_type=gene&page_num=0 '' MCOLN3 '']||[http://mouse.brain-map.org/experiment/show/75934924 '' Mcoln3 '']|| 定常活性化 || PI(3,5)P2、ML SA1、SF-21、SF-11、[[SF-1]]、[[SF-2]]、[[MK6-83]]、 || ベラパミル、Gd<sup>3+</sup>、細胞外酸性化、Na+ || [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/5W3S 5W3S] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| 151行目: | 151行目: | ||
機能的にTRPC1は[[脳由来神経栄養因子]](BDNF)や[[ネトリン-1]]による[[軸索誘導]]に関係している<ref><PUBMED>15758952</PUBMED></ref><ref><PUBMED>19945390 </PUBMED></ref>。また、培養された海馬ニューロンでは、TRPC4の発現は[[神経突起]]伸長・分岐を阻害し<ref><PUBMED>24011658</PUBMED></ref>、TRPC5もまた神経突起伸長や[[成長円錐]]形態を阻害することが知られている<ref><PUBMED>12858178</PUBMED></ref>。これらの知見により、TRPC4/TRPC5は適切な脳の発達に必要な神経突起伸長に対する負の制御において重要な役割を担っていると考えられる。 | 機能的にTRPC1は[[脳由来神経栄養因子]](BDNF)や[[ネトリン-1]]による[[軸索誘導]]に関係している<ref><PUBMED>15758952</PUBMED></ref><ref><PUBMED>19945390 </PUBMED></ref>。また、培養された海馬ニューロンでは、TRPC4の発現は[[神経突起]]伸長・分岐を阻害し<ref><PUBMED>24011658</PUBMED></ref>、TRPC5もまた神経突起伸長や[[成長円錐]]形態を阻害することが知られている<ref><PUBMED>12858178</PUBMED></ref>。これらの知見により、TRPC4/TRPC5は適切な脳の発達に必要な神経突起伸長に対する負の制御において重要な役割を担っていると考えられる。 | ||
ノックアウトマウスを用いた実験により、TRPC1/TRPC4/TRPC5およびTRPC3/TRPC6は、[[てんかん]]に関連しているという報告もある<ref><PUBMED>22144671</PUBMED></ref><ref><PUBMED>23188715</PUBMED></ref><ref><PUBMED>22926417</PUBMED></ref><ref><PUBMED>23529532</PUBMED></ref>。 | |||
TRPC3は[[前頭前皮質]]と小脳に発現している。特に小脳では[[プルキンエ細胞]]に豊富に発現しており、[[代謝型グルタミン酸受容体]]依存的なシナプスのシグナル伝達に重要であるため、歩行などの運動の協調性を制御する<ref><PUBMED>19741172</PUBMED></ref>。 | TRPC3は[[前頭前皮質]]と小脳に発現している。特に小脳では[[プルキンエ細胞]]に豊富に発現しており、[[代謝型グルタミン酸受容体]]依存的なシナプスのシグナル伝達に重要であるため、歩行などの運動の協調性を制御する<ref><PUBMED>19741172</PUBMED></ref>。 | ||
| 164行目: | 164行目: | ||
=== TRPM === | === TRPM === | ||
TRPM2は、海馬、大脳皮質、[[黒質]]、TRPM3は、海馬、[[脳梁]]、大脳皮質、TRPM4は[[視床]]、[[視床下部]]、[[延髄]] | TRPM2は、海馬、大脳皮質、[[黒質]]、TRPM3は、海馬、[[脳梁]]、大脳皮質、TRPM4は[[視床]]、[[視床下部]]、[[延髄]]、海馬などに発現している。TRPM6のmRNAは低いレベルでの脳での発現が報告されているが、中枢神経での役割はまだ分かっていない。TRPM7のmRNAは脳において高発現しており、ラットの脳において海馬錐体ニューロンでの発現が報告されている。 | ||
TRPM2は海馬[[シナプス可塑性]]への関与の可能性が示唆されている<ref><PUBMED>22188973</PUBMED></ref>。さらに、TRPM2は神経発達に関連しており、発達神経突起伸長において阻害的な役割を担う<ref><PUBMED>24413888</PUBMED></ref>。 | TRPM2は海馬[[シナプス可塑性]]への関与の可能性が示唆されている<ref><PUBMED>22188973</PUBMED></ref>。さらに、TRPM2は神経発達に関連しており、発達神経突起伸長において阻害的な役割を担う<ref><PUBMED>24413888</PUBMED></ref>。 | ||
2019年1月26日 (土) 13:05時点における版
黒川 竜紀
大分大学医学部
森 泰生
京都大学大学院工学研究科
DOI:10.14931/bsd.7776 原稿受付日:2018年10月19日 原稿完成日:2018年X月X日
担当編集委員:林 康紀(京都大学大学院医学研究科システム神経薬理分野)
英:transient receptor potential channel 独:Transiente Rezeptor-Potential Ionenkanal
Transient receptor potential(TRP)チャネルは、6回膜貫通領域を有するTRPタンパク質群のホモあるいはヘテロ4量体によりなる多様な陽イオンチャネルである。TRPチャネルの活性化開口は、温度、機械刺激、痛み、酸-塩基といった種々の物理化学的刺激によって惹起され、多くが高いNa+及びCa2+透過能を示す。様々な組織にTRPチャネルは分布するが、中枢・末梢神経系において高発現する。神経機能に重要な役割を果たすTRPチャネルがいくつか存在しており、それらの機能障害は、神経変性疾患や精神疾患など様々な病気に関連している。
| Transient receptor potential (TRP) ion channel | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | TRP | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF06011 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR010308 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 8 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 3j5p | ||||||||
| Membranome | 605 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Transient receptor potentialチャネルとは
TRPは、元来、1989年にショウジョウバエの光受容応答変異株の原因遺伝子として発見された遺伝子名である[1] 。命名は、trp変異株で光受容器電位(receptor potential)変化が一過性(transient)であることに由来する。TRP遺伝子により構成されるイオンチャネルは多くがNa+及びCa2+の透過性が高い陽イオンチャネルであるが、Ca2+選択性は大きく異なる[2] 。
TRPチャネルはPIP2、Ca2+、環状ヌクレオチドなどの細胞のシグナル伝達因子や、温度、浸透圧などの環境因子などに応答することから、物理学的・化学的刺激に対して広い範囲で応答するセンサーとして機能している[3] 。TRPチャネルの活性化開口により、膜電位の変化、Ca2+の細胞内流入によるCa2+依存性経路の活性化、酵素活性の変化、エンドサイトーシス・エキソサイトーシスなどの細胞応答が引き起こされる。このため、TRPチャネルは、受精、感覚変換、細胞生存、発生など生命の基本的過程において重要な役割を担うことができる[4] 。
構造
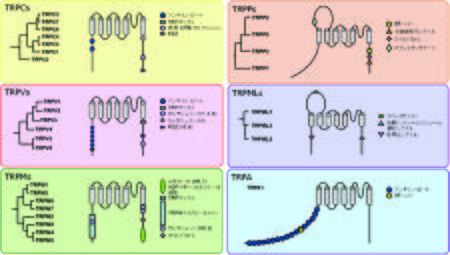
TRPの基本構造は6回膜貫通領域でおり、ホモあるいはヘテロ4量体を形成することによりイオンチャネルを形成している。また、細胞質領域であるN末端及びC末端側それぞれに特徴的な構造を有しており、それらはチャネル活性の調節に重要である(図1)。
N末端領域には、TRPC、TRPV、TRPAにおいてアンキリンリピートドメインを有する。TRPC、TRPM、TRPVのC末端領域には、TRP-ボックスを含む25アミノ酸残基からなるTRPドメインが存在する。また、C末端部位には、TRPP、TRPMLの小胞体移行シグナル、TRPM2、TRPM6、TRPM7の酵素活性部位など特徴的なドメインが見られる。
TRPチャネルは、電位依存性チャネルと同じく6回膜貫通型のチャネルであるが、TRPV1、TRPM4、TRPM5、TRPM8、TRPA1など一部のTRPチャネルのみ膜電位変化によって活性化することが知られている。電位依存性チャネルの第4番目の膜貫通領域には電位変化の感知に重要な正電荷を持ったアミノ酸残基が多く存在するが、TRPチャネルではTRPPを除きさほど明確ではない。
近年、電子線直接検出カメラと電子顕微鏡を組み合わせた単粒子解析により、多くのTRPチャネルで高解像度の立体構造が報告されており、構造を基とした機能解析が可能になりつつある[5] 。
ファミリー
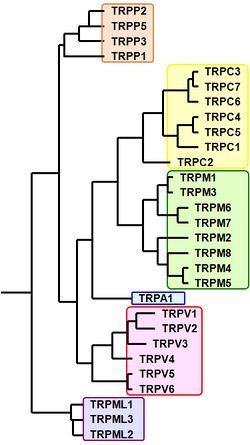
TRPタンパク質はTRPC(canonical)、TRPM(melastatin)、TRPV(vanilloid)、TRPML(mucolipin)、TRPP(polycystin)、TPRA(ankyrin)、TRPN(nompC:no mechanoreceptor potential C)の7つのサブファミリーを構成しているが、哺乳類では28種のホモログが同定され、TRPNサブファミリーを除く6つのサブファミリーを構成している[6][7](図2、表) 。ヒトにおいては、TRPC2が偽遺伝子となっているため27種類のホモログが存在する。
TRPC
TRPCファミリーは、初めて同定されたショウジョウバエTRPと最も相同性が高く、7つのホモログが報告されている。ヒトでは、TRPC1、TRPC3、TRPC4、TRPC5、TRPC6とTRPC7が存在しており、マウスや他の種で見つかっているTRPC2においては偽遺伝子になっており発現していない。
TRPCチャネルはホスホリパーゼの活性化に伴って活性化開口する受容体活性化型陽イオンチャネルであるが、直接的な活性化の引き金は様々である。
TRPM
TRPMファミリーは、他のTRPファミリーに比べて最も多様性が高いサブファミリーである。最初に発見されたTRPM1は、名前の由来の通り(TRP melastatin 1)、メラノーマ細胞における腫瘍の悪性度に反比例して発現が減少するが[8] 、その機能的特徴は不明な点が多い。
TRPMファミリーには、酵素ドメインが進化的に融合した種類も存在し、TRPM2には、ADPリボースピロホスファターゼであるNUDT9-Hドメインが[9] 、TRPM6とTRPM7には、機能的なキナーゼモチーフが存在する[10] 。
TRPM8はTRPMファミリーの中で最も研究が進んでおり、冷温センサーとして働くことがわかっている[11] 。
TRPV
TRPVファミリーは、最初に同定されたTRPV1(TRP vanilloid 1)がバニロイド類に属すカプサイシンの受容体であることから命名されたが[12] 、TRPVファミリーの中でバニロイド類により活性化されるのはTRPV1のみである。
TRPV1は、感覚神経において高い発現を示し、痛みの原因物質として考えられている酸や熱によって活性化する[12][13] 。TRPファミリーにおいて初めて高解像度の立体構造が明らかになったのはTRPV1であり、この構造によりTRPは6回膜貫通ドメインを持つサブユニットが4量体を形成していることが再確認された[14] 。
TRPVファミリーには、TRPV4のように機械受容チャネルも存在する[15] 。
TRPVファミリーの多くは、Ca2+依存的な制御を受けており[16] 、TRPV5とTRPV6はカルモデュリンにより直接制御を受けることが報告されている[17] 。
TRPML
TRPMLファミリーは、TRPML1がムコリピドーシスIV型の原因遺伝子として同定されたことから命名された[18] 。TRPMLファミリーはリソソームに局在しており[19] 、PIP2により制御されることが知られている[20] 。
TRPP
TRPPファミリーは、TRPP2(PKD2、polycystin-2)、TRPP3 (PKD2L1、polycystin-L)、TRPP5 (PKD2L2)から構成されており、TRPP2の変異は常染色体優性多発性嚢胞腎(ADPKD)を引き起こす[21] 。TRPP2は、ADPKDの主要原因遺伝子がコードするPKD1(polycystin-1)と相互作用する[22] 。この複合体形成は、TRPP2がチャネルとして機能するために必要だと考えられてきたが、必ずしもこの考えは認知されているわけではない[23] 。
TRPP3は、舌の味細胞においてPKD1L3と共発現しており、酸味受容に関わっている[24] 。
TPRA
TRPAは、N末端に多くのアンキリンリピートドメインを持つことから命名されており、哺乳類においては、現在のところTRPA1の1種類だけが同定されている。
他のTRPファミリーにおいてもアンキリンリピートドメインを持つものは多いが、TRPA1では少なくとも14個のアンキリンリピートドメインを持っており、同定されている哺乳類のTRPファミリーの中で最も多い。TRPA1遺伝子は、ハエから哺乳類まで保存されており、ヒトのTRPA1においては感覚神経に高発現している。
TRPVやTRPMファミリーと同じように、TRPA1の活性は温度により制御されるが、この温度感受性は種によりかなり異なっている[25] 。
脳における機能と病気との関連
TRPC
すべてのTRPCチャネルが脳の様々な領域に発現しており[26] 、一般的には受容体活性化型陽イオンチャネルとして機能している。マウスにおいてTRPC1は小脳、海馬、大脳基底核、扁桃体、前脳など様々な領域で、TRPC4は、海馬、大脳皮質、小脳で発現が確認されている。
TRPC1とTRPC5の発現部位が似ていることから、TRPC1とTRPC5によるヘテロマーチャネルの形成が疑われたが、十分な証拠は今のところ得られていない。
機能的にTRPC1は脳由来神経栄養因子(BDNF)やネトリン-1による軸索誘導に関係している[27][28]。また、培養された海馬ニューロンでは、TRPC4の発現は神経突起伸長・分岐を阻害し[29]、TRPC5もまた神経突起伸長や成長円錐形態を阻害することが知られている[30]。これらの知見により、TRPC4/TRPC5は適切な脳の発達に必要な神経突起伸長に対する負の制御において重要な役割を担っていると考えられる。
ノックアウトマウスを用いた実験により、TRPC1/TRPC4/TRPC5およびTRPC3/TRPC6は、てんかんに関連しているという報告もある[31][32][33][34]。
TRPC3は前頭前皮質と小脳に発現している。特に小脳ではプルキンエ細胞に豊富に発現しており、代謝型グルタミン酸受容体依存的なシナプスのシグナル伝達に重要であるため、歩行などの運動の協調性を制御する[35]。
TRPC3とTRPC6は、小脳顆粒細胞においてBDNFによる神経保護に関して重要な役割を担っている[36]。
ラットの海馬においてTRPC6は興奮性後シナプスに局在しており、TRPC6の過剰発現は、海馬ニューロンにおけるスパインの数を増加させ、モリス水迷路試験において空間認知・空間記憶を増強させることから、TRPC6はシナプス可塑性と行動可塑性において機能的な役割を担うと考えられる[37][38]。
TRPC3は、プロテインキナーゼC(PKC)γの変異から生じる脊髄小脳運動失調症 (spinocerebellar ataxia type 14)と関係していると考えられている[39]。
ピロカルピン誘導てんかん重積状態ラットでは、歯状回顆粒細胞だけでなくCA1、CA3錐体細胞においても、TRPC3の発現は著しく増強されるがTRPC6は減少することから、TRPC3はてんかん重積状態において有害な役割を担うと考えられる[40]。
TRPM
TRPM2は、海馬、大脳皮質、黒質、TRPM3は、海馬、脳梁、大脳皮質、TRPM4は視床、視床下部、延髄、海馬などに発現している。TRPM6のmRNAは低いレベルでの脳での発現が報告されているが、中枢神経での役割はまだ分かっていない。TRPM7のmRNAは脳において高発現しており、ラットの脳において海馬錐体ニューロンでの発現が報告されている。
TRPM2は海馬シナプス可塑性への関与の可能性が示唆されている[41]。さらに、TRPM2は神経発達に関連しており、発達神経突起伸長において阻害的な役割を担う[42]。
脳におけるβアミロイドの蓄積による神経細胞死は、アルツハイマー病において重要な要因だと認識されているが、このβアミロイドの蓄積は、活性酸素種 (ROS)産生とCa2+恒常性の調節異常と関連があると考えられている。アルツハイマー病モデルにおいて、TRPM2を欠損させることにより、小胞体ストレス反応や神経変性、異常なミクログリア活性などが減少し、空間記憶障害の改善など見られることから、TRPM2の異常な活性化がアルツハイマー病の病理学的事象につながると考えられている[43] 。
また、酸化ストレスによるTRPM2の活性化は神経において細胞死につながることから、TRPM2はパーキンソン病に関係している可能性が考えられる。グアム型筋委縮性側索硬化症-パーキンソン認知症複合(Guamanian amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism dementia complex: ALS/PDC)の患者では、TRPM2とTRPM7において変異が見つかっていることから、これらのチャネルを介したイオン流入が生理的に重要であり、その乱れが病態に関わっている可能性を示唆している[44] 。一方、ALS/PDCの患者が集積する紀伊半島南部における連鎖解析では、TRPM7遺伝子座の関与を示すデータが得られなかったことから、これらの患者集団ではTRPM7は関係しているという証拠はない[45] 。
精神疾患に関しては、I型双極性障害(bipolar disorder type I: BD)の患者においてTRPM2の変異が報告されており、TRPM2の機能とBDの病状との関係が示唆されている[46] 。
TRPV
TRPV1は海馬錐体ニューロン、歯状回、青斑核、視床下部、黒質、小脳、大脳皮質などに発現しており、TRPV2も広く脳で発現している。また、TRPV3のmRNAは、大脳皮質、海馬、視床、線条体、小脳、TRPV4のmRNAは、視床下部、小脳、大脳基底核、海馬錐体ニューロンで検出されている。さらに、アストロサイトでは、TRPV1、TRPV2、TRPV3、TRPV4が発現している。
TRPV1は神経活動やシナプス可塑性の制御において重要な役割を担っており、TRPV1の活性化は、海馬介在ニューロンにおける興奮性シナプスの長期抑圧(long term depression: LTD)の引き金となる[47]。さらに、TRPV1は脳において興奮伝達を促進し、長期増強(long term potentiation: LTP)を誘起する[48]。
発熱時には体温を下げるため発汗の増加が起こるが、それと同時に視床下部より分泌されるバソプレシンが腎臓での水の再吸収を増加させることにより体内の水分を調整している。TRPV1のノックアウトマウスでは、発熱時におけるバソプレシンの分泌が抑制されることから、視床下部のバソプレシン産生ニューロンの温度感受性にはTRPV1が寄与していると示唆されている[49]。
内側側頭葉てんかんの患者の大脳皮質や海馬では、TRPV1の発現が著しく上昇していることから、TRPV1はてんかんに関連している可能性が示唆されている[50]。
行動試験では、TRPV1アゴニストの投与は不安惹起作用があるが、TRPV1アンタゴニストは抗不安作用があったことから、TRPV1の活性化は、不安惹起作用を引き起こす可能性が示唆されている[51]。
関連項目
参考文献
- ↑
Montell, C., & Rubin, G.M. (1989).
Molecular characterization of the Drosophila trp locus: a putative integral membrane protein required for phototransduction. Neuron, 2(4), 1313-23. [PubMed:2516726] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Mulier, M., Vriens, J., & Voets, T. (2017).
TRP channel pores and local calcium signals. Cell calcium, 66, 19-24. [PubMed:28807146] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Clapham, D.E. (2003).
TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature, 426(6966), 517-24. [PubMed:14654832] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ Sawamura S, Shirakawa H, Nakagawa T, Mori Y, Kaneko S.
TRP Channels in the Brain: What Are They There For?.
In: Emir TLR, editor. Neurobiology of TRP Channels. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2017. Chapter 16., Frontiers in Neuroscience - ↑
Madej, M.G., & Ziegler, C.M. (2018).
Dawning of a new era in TRP channel structural biology by cryo-electron microscopy. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology, 470(2), 213-225. [PubMed:29344776] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ 富永 真琴
TRPチャネル研究の現在と未来
実験医学 32, 504-511, 2014 - ↑
Numata, T., Kozai, D., Takahashi, N., Kato, K., Uriu, Y., Yamamoto, S., ..., & Mori, Y. (2009).
[Structures and variable functions of TRP channels]. Seikagaku. The Journal of Japanese Biochemical Society, 81(11), 962-83. [PubMed:19999578] [WorldCat] - ↑
Duncan, L.M., Deeds, J., Hunter, J., Shao, J., Holmgren, L.M., Woolf, E.A., ..., & Shyjan, A.W. (1998).
Down-regulation of the novel gene melastatin correlates with potential for melanoma metastasis. Cancer research, 58(7), 1515-20. [PubMed:9537257] [WorldCat] - ↑
Kühn, F.J., & Lückhoff, A. (2004).
Sites of the NUDT9-H domain critical for ADP-ribose activation of the cation channel TRPM2. The Journal of biological chemistry, 279(45), 46431-7. [PubMed:15347676] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Runnels, L.W., Yue, L., & Clapham, D.E. (2001).
TRP-PLIK, a bifunctional protein with kinase and ion channel activities. Science (New York, N.Y.), 291(5506), 1043-7. [PubMed:11161216] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
McKemy, D.D., Neuhausser, W.M., & Julius, D. (2002).
Identification of a cold receptor reveals a general role for TRP channels in thermosensation. Nature, 416(6876), 52-8. [PubMed:11882888] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ 12.0 12.1
Caterina, M.J., Schumacher, M.A., Tominaga, M., Rosen, T.A., Levine, J.D., & Julius, D. (1997).
The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 389(6653), 816-24. [PubMed:9349813] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Davis, J.B., Gray, J., Gunthorpe, M.J., Hatcher, J.P., Davey, P.T., Overend, P., ..., & Sheardown, S.A. (2000).
Vanilloid receptor-1 is essential for inflammatory thermal hyperalgesia. Nature, 405(6783), 183-7. [PubMed:10821274] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Liao, M., Cao, E., Julius, D., & Cheng, Y. (2013).
Structure of the TRPV1 ion channel determined by electron cryo-microscopy. Nature, 504(7478), 107-12. [PubMed:24305160] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Strotmann, R., Harteneck, C., Nunnenmacher, K., Schultz, G., & Plant, T.D. (2000).
OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nature cell biology, 2(10), 695-702. [PubMed:11025659] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Gordon-Shaag, A., Zagotta, W.N., & Gordon, S.E. (2008).
Mechanism of Ca(2+)-dependent desensitization in TRP channels. Channels (Austin, Tex.), 2(2), 125-9. [PubMed:18849652] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Lambers, T.T., Weidema, A.F., Nilius, B., Hoenderop, J.G., & Bindels, R.J. (2004).
Regulation of the mouse epithelial Ca2(+) channel TRPV6 by the Ca(2+)-sensor calmodulin. The Journal of biological chemistry, 279(28), 28855-61. [PubMed:15123711] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Slaugenhaupt, S.A. (2002).
The molecular basis of mucolipidosis type IV. Current molecular medicine, 2(5), 445-50. [PubMed:12125810] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Venkatachalam, K., Wong, C.O., & Zhu, M.X. (2015).
The role of TRPMLs in endolysosomal trafficking and function. Cell calcium, 58(1), 48-56. [PubMed:25465891] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Dong, X.P., Shen, D., Wang, X., Dawson, T., Li, X., Zhang, Q., ..., & Xu, H. (2010).
PI(3,5)P(2) controls membrane trafficking by direct activation of mucolipin Ca(2+) release channels in the endolysosome. Nature communications, 1, 38. [PubMed:20802798] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Ong, A.C., & Harris, P.C. (2015).
A polycystin-centric view of cyst formation and disease: the polycystins revisited. Kidney international, 88(4), 699-710. [PubMed:26200945] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Hanaoka, K., Qian, F., Boletta, A., Bhunia, A.K., Piontek, K., Tsiokas, L., ..., & Germino, G.G. (2001).
Co-assembly of polycystin-1 and -2 produces unique cation-permeable currents. Nature, 408(6815), 990-4. [PubMed:11140688] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Shen, P.S., Yang, X., DeCaen, P.G., Liu, X., Bulkley, D., Clapham, D.E., & Cao, E. (2016).
The Structure of the Polycystic Kidney Disease Channel PKD2 in Lipid Nanodiscs. Cell, 167(3), 763-773.e11. [PubMed:27768895] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Ishimaru, Y., Inada, H., Kubota, M., Zhuang, H., Tominaga, M., & Matsunami, H. (2006).
Transient receptor potential family members PKD1L3 and PKD2L1 form a candidate sour taste receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103(33), 12569-74. [PubMed:16891422] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Laursen, W.J., Anderson, E.O., Hoffstaetter, L.J., Bagriantsev, S.N., & Gracheva, E.O. (2016).
Species-specific temperature sensitivity of TRPA1. Temperature (Austin, Tex.), 2(2), 214-26. [PubMed:27227025] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Vennekens, R., Menigoz, A., & Nilius, B. (2012).
TRPs in the Brain. Reviews of physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology, 163, 27-64. [PubMed:23184016] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Li, Y., Jia, Y.C., Cui, K., Li, N., Zheng, Z.Y., Wang, Y.Z., & Yuan, X.B. (2005).
Essential role of TRPC channels in the guidance of nerve growth cones by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature, 434(7035), 894-8. [PubMed:15758952] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Shim, S., Yuan, J.P., Kim, J.Y., Zeng, W., Huang, G., Milshteyn, A., ..., & Worley, P.F. (2009).
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase FKBP52 controls chemotropic guidance of neuronal growth cones via regulation of TRPC1 channel opening. Neuron, 64(4), 471-83. [PubMed:19945390] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Jeon, J.P., Roh, S.E., Wie, J., Kim, J., Kim, H., Lee, K.P., ..., & So, I. (2013).
Activation of TRPC4β by Gαi subunit increases Ca2+ selectivity and controls neurite morphogenesis in cultured hippocampal neuron. Cell calcium, 54(4), 307-19. [PubMed:24011658] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Greka, A., Navarro, B., Oancea, E., Duggan, A., & Clapham, D.E. (2003).
TRPC5 is a regulator of hippocampal neurite length and growth cone morphology. Nature neuroscience, 6(8), 837-45. [PubMed:12858178] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Phelan, K.D., Mock, M.M., Kretz, O., Shwe, U.T., Kozhemyakin, M., Greenfield, L.J., ..., & Zheng, F. (2012).
Heteromeric canonical transient receptor potential 1 and 4 channels play a critical role in epileptiform burst firing and seizure-induced neurodegeneration. Molecular pharmacology, 81(3), 384-92. [PubMed:22144671] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Phelan, K.D., Shwe, U.T., Abramowitz, J., Wu, H., Rhee, S.W., Howell, M.D., ..., & Zheng, F. (2013).
Canonical transient receptor channel 5 (TRPC5) and TRPC1/4 contribute to seizure and excitotoxicity by distinct cellular mechanisms. Molecular pharmacology, 83(2), 429-38. [PubMed:23188715] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Kim, D.S., Ryu, H.J., Kim, J.E., & Kang, T.C. (2013).
The reverse roles of transient receptor potential canonical channel-3 and -6 in neuronal death following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Cellular and molecular neurobiology, 33(1), 99-109. [PubMed:22926417] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Ryu, H.J., Kim, J.E., Kim, Y.J., Kim, J.Y., Kim, W.I., Choi, S.Y., ..., & Kang, T.C. (2013).
Endothelial transient receptor potential conical channel (TRPC)-3 activation induces vasogenic edema formation in the rat piriform cortex following status epilepticus. Cellular and molecular neurobiology, 33(4), 575-85. [PubMed:23529532] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Glitsch, M.D. (2010).
Activation of native TRPC3 cation channels by phospholipase D. FASEB journal : official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 24(1), 318-25. [PubMed:19741172] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Jia, Y., Zhou, J., Tai, Y., & Wang, Y. (2007).
TRPC channels promote cerebellar granule neuron survival. Nature neuroscience, 10(5), 559-67. [PubMed:17396124] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Tai, Y., Feng, S., Ge, R., Du, W., Zhang, X., He, Z., & Wang, Y. (2008).
TRPC6 channels promote dendritic growth via the CaMKIV-CREB pathway. Journal of cell science, 121(Pt 14), 2301-7. [PubMed:18559891] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Zhou, J., Du, W., Zhou, K., Tai, Y., Yao, H., Jia, Y., ..., & Wang, Y. (2008).
Critical role of TRPC6 channels in the formation of excitatory synapses. Nature neuroscience, 11(7), 741-3. [PubMed:18516035] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Shuvaev, A.N., Horiuchi, H., Seki, T., Goenawan, H., Irie, T., Iizuka, A., ..., & Hirai, H. (2011).
Mutant PKCγ in spinocerebellar ataxia type 14 disrupts synapse elimination and long-term depression in Purkinje cells in vivo. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 31(40), 14324-34. [PubMed:21976518] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Kim, D.S., Ryu, H.J., Kim, J.E., & Kang, T.C. (2013).
The reverse roles of transient receptor potential canonical channel-3 and -6 in neuronal death following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Cellular and molecular neurobiology, 33(1), 99-109. [PubMed:22926417] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Xie, Y.F., Belrose, J.C., Lei, G., Tymianski, M., Mori, Y., Macdonald, J.F., & Jackson, M.F. (2011).
Dependence of NMDA/GSK-3β mediated metaplasticity on TRPM2 channels at hippocampal CA3-CA1 synapses. Molecular brain, 4, 44. [PubMed:22188973] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Jang, Y., Lee, M.H., Lee, J., Jung, J., Lee, S.H., Yang, D.J., ..., & Oh, U. (2014).
TRPM2 mediates the lysophosphatidic acid-induced neurite retraction in the developing brain. Pflugers Archiv : European journal of physiology, 466(10), 1987-98. [PubMed:24413888] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Yamamoto, S., Wajima, T., Hara, Y., Nishida, M., & Mori, Y. (2007).
Transient receptor potential channels in Alzheimer's disease. Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1772(8), 958-67. [PubMed:17490865] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Hermosura, M.C., & Garruto, R.M. (2007).
TRPM7 and TRPM2-Candidate susceptibility genes for Western Pacific ALS and PD? Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1772(8), 822-35. [PubMed:17395433] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Hara, K., Kokubo, Y., Ishiura, H., Fukuda, Y., Miyashita, A., Kuwano, R., ..., & Tsuji, S. (2010).
TRPM7 is not associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism dementia complex in the Kii peninsula of Japan. American journal of medical genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric genetics : the official publication of the International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, 153B(1), 310-3. [PubMed:19405049] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Roedding, A.S., Gao, A.F., Au-Yeung, W., Scarcelli, T., Li, P.P., & Warsh, J.J. (2012).
Effect of oxidative stress on TRPM2 and TRPC3 channels in B lymphoblast cells in bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorders, 14(2), 151-61. [PubMed:22420591] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Gibson, H.E., Edwards, J.G., Page, R.S., Van Hook, M.J., & Kauer, J.A. (2008).
TRPV1 channels mediate long-term depression at synapses on hippocampal interneurons. Neuron, 57(5), 746-59. [PubMed:18341994] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Marinelli, S., Di Marzo, V., Berretta, N., Matias, I., Maccarrone, M., Bernardi, G., & Mercuri, N.B. (2003).
Presynaptic facilitation of glutamatergic synapses to dopaminergic neurons of the rat substantia nigra by endogenous stimulation of vanilloid receptors. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 23(8), 3136-44. [PubMed:12716921] [PMC] [WorldCat] - ↑
Sharif-Naeini, R., Ciura, S., & Bourque, C.W. (2008).
TRPV1 gene required for thermosensory transduction and anticipatory secretion from vasopressin neurons during hyperthermia. Neuron, 58(2), 179-85. [PubMed:18439403] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Sun, F.J., Guo, W., Zheng, D.H., Zhang, C.Q., Li, S., Liu, S.Y., ..., & Shu, H.F. (2013).
Increased expression of TRPV1 in the cortex and hippocampus from patients with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Journal of molecular neuroscience : MN, 49(1), 182-93. [PubMed:22936245] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Fogaça, M.V., Aguiar, D.C., Moreira, F.A., & Guimarães, F.S. (2012).
The endocannabinoid and endovanilloid systems interact in the rat prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex to control anxiety-like behavior. Neuropharmacology, 63(2), 202-10. [PubMed:22691536] [WorldCat] [DOI]