Zic
有賀 純、畑山 実
長崎大学大学院医歯薬学総合研究科
DOI:10.14931/bsd.6899 原稿受付日:2016年2月8日 原稿完成日:2016年月日
担当編集委員:村上 富士夫(大阪大学 大学院生命機能研究科)
Zic(Zinc-finger protein of the cerebellum)とは進化的に保存された亜鉛フィンガー(zinc finger)を持つタンパク質をコードする遺伝子の一群で、神経発生や初期発生に関わる細胞分化を制御することが知られている。その機能不全は、前脳や小脳の形成障害、内臓左右軸異常などの原因となる[1] [2] [3] [4]。
生物における分布
カイメン動物および有櫛動物を除く後生動物(metazoa)に存在することが確認されている[5] [6]。哺乳類では5種類の関連遺伝子(Zic1-Zic5)が存在する。各動物における相同遺伝子、関連遺伝子を総称してZicファミリーと呼ぶ。ショウジョウバエ、クモのOdd-paired、線虫のREF-2、ホヤのmacho-1もZicファミリーに含まれる。
構造
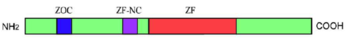
「システイン-Xn-システイン-Xn-ヒスチジン-Xn-ヒスチジン」のモチーフが5回繰り返すC2H2型の亜鉛(Zn)フィンガードメインは全てのZicファミリータンパク質で保存されている。その他にN末のZOC(Zic-Opa conserved)ドメインとZFNC(Zinc finger N–terminus conserved)ドメインが多くのZicファミリータンパク質で保存された構造として知られている(図)。各動物グループ(門)間における保存性の差異の存在が提唱されている[5]。Zicファミリーの亜鉛フィンガードメインはGliファミリーおよびGlisファミリーのものと類似しており、3グループを総称して、Gli(-Glis-Zic)スーパーファミリーと呼ぶこともある。
分子機能
亜鉛フィンガーを介してDNAと結合するほか、転写の共役因子、クロマチン再構成因子と結合して、遺伝子の発現を制御することが知られている。転写活性とは関係無しに非対称性分裂を制御する機序も報告されている[7]。
hedgehog シグナル、Wntシグナル、TGFβシグナル、レチノイン酸シグナルなどの生体情報系と関係を持つことが知られている。核に存在する場合が多いが、ヒト先天奇形の患者由来の変異体の一部は細胞内局在の異常を示す。
発生における役割
神経系の発生
神経誘導
(神経外胚葉への分化)
ツメガエルの解析から、神経誘導の際に予定神経板領域に発現が誘導され、その発現により、神経系細胞への分化が促進されることが分かっている。ホヤや線虫などの動物においても、神経系の細胞が産み出される際に役割を持つことが知られている[8]。
神経堤細胞の産生
ツメガエル神経板境界部ではZicファミリー遺伝子が発現しており、過剰発現することで、神経堤領域の拡大が起きる。ツメガエル胚では神経堤細胞の産生にPax3とZic1が協調的に働く[9]。
神経管形成
Zicファミリー遺伝子は背側神経管で発現しており、Zic2機能低下マウスとZic3機能喪失マウスでは神経管の閉鎖不全による二分脊椎症が観察される。ヒトの神経管奇形発症への関与は認められていない[10]。
前脳の発生
ZIC2が全前脳症という前脳正中部の形成障害を伴う先天性奇形の原因遺伝子となることが知られている。染色体異常の無い全前脳症患者のうち、6-8%にZIC2の点突然変異または微小な欠失が認められ、この頻度は別の全前脳症原因遺伝子SHHに次いで2番目に多い[11]。Zic2発現低下マウスでも左右の脳室の融合が見られる。奇形の発症機序として前脳の形態形成を制御する脊索前板の発生障害が提唱されている[12]。
小脳の発生
ZIC1は小脳虫部の形成障害を主徴とするDandy-Walker症候群の原因遺伝子の1つである[13]。3q24-25欠失を伴う8症例において、ZIC1とZIC4のヘテロ欠失が報告されている。Zic1, Zic2は発生過程の小脳において強い発現があり、それらの機能が失われたマウスでは小脳の形成異常が生じる。成熟個体の小脳では顆粒細胞にZic1,Zic2の強い発現があり、マーカーとして用いられることもある。
神経細胞のネットワーク形成
Zic2は腹外側部の網膜神経節細胞において発現しており、同部位からの軸索は視交叉において同側の外側膝状体へと投射し、それ以外の部位のものは反対側へと投射する。これが深さや奥行きを認知する「両眼視」機能の成り立ちに必要であることが知られている。同様に脊髄における同側あるいは反対側への投射の選択にもZic2の機能が関与することが報告されている[14]。これらの軸索走向の決定にはZic2がEphファミリータンパク質の発現を制御することが部分的に関係するものと考えられている。
髄膜の発生
Zic1, Zic2, Zic3は髄膜の前駆細胞に発現していることが知られており、Zic2発現低下マウス、Zic1欠失変異・Zic3欠失変異複合変異マウスでは髄膜の発生に異常が生じることが報告されている。これに伴い、基底膜の断裂が生じること、髄膜から分泌される分泌因子の発現が低下すること、大脳皮質の表層に沿った神経細胞の移動に異常が生じることが報告されている[15]。
神経系以外の発生における役割
中胚葉の産生
マウス、ツメガエルではZicファミリーが将来、体節や骨、筋肉を形成する中胚葉が形成される時期に発現しており、Zic2発現低下・Zic3欠失複合変異マウスでは初期中胚葉の産生に障害がおきる[16]。
左右軸決定
ZIC3は内臓左右不定位症(ヘテロタキシー、heterotaxy, situs ambiguous)と心奇形(一部の完全大動脈転位症、両大血管右室起始症)の原因遺伝子である。散発性のヘテロタキシーの3.7%でZIC3の変異が認められる[17]。マウスでは左右軸の決定に重要な役割を果たすと考えられているノード(node)の形成にZic3が必要であることが示されている[18]。
脊索の形成
ツメガエルZic3やホヤZicファミリーは脊索の発生に重要な役割を持つことが示されている[19] [20]。
分節構造の形成
脊椎動物ではZicファミリーは体節に発現し、その形成と分化を制御する。ショウジョウバエとクモのOdd-pairedは体の前後軸に沿った分節の際に発現しており、分節形成に関与する[21]。有爪動物(カギムシ)と環形動物(イトミミズ)でも分節構造の形成の際に発現する[22] [23]。
骨格系の形態形成
Zic1、Zic2、Zic3、またはZic5を欠損するマウスでは、脊椎・椎弓、肋骨、顎骨、四肢骨の形態異常が認められる。硬骨魚類の尾びれの背腹軸に沿った非対称性の成り立ちにZic1、Zic4が関わり[24]、体節を背側化するスイッチとしての役割を果たす[25]。椎弓の形成においてはZic1とGli3が協調的に働き、肢芽の形態形成においてはZic3とGli3が拮抗的に働くことが示されている[26]。
筋肉系の分化
Zic2の発現低下マウスでは筋肉の発生に異常が生じる[27]。ホヤのmacho-1は筋肉への分化を制御する[28]。
高次脳機能の成り立ちにおける役割
Zic2発現低下マウスでは、新規環境での過活動、認知機能の異常、社会性行動の異常が認められている[29]。一例の統合失調症の患者から、ZIC2の機能低下型変異が見つかっている[29]。早期統合失調症患者の末梢血リンパ球でZIC2の発現が低下していることが報告されている[30]。また、Zic1発現低下マウス、Zic3欠失マウスでは筋緊張度の低下が表れる。Zic3欠失マウスでは動眼調節機能の異常が認められている[31]。ZIC1のC末欠失型変異が学習障害と関連することも知られている[32]。
幹細胞制御における役割
胚性幹細胞の分化制御
胚性幹細胞にZic2, Zic3の発現があり、Zic3は内胚葉への分化を妨げることにより、多分化能を維持している [33]。また、Zic2は胚性幹細胞からの神経分化に必要であることも示されている[34]。
ガン幹細胞
髄芽細胞腫、髄膜腫、脂肪肉腫、肝細胞癌、胃癌、膵管癌、肺癌、大腸癌、子宮頚癌、卵巣癌などにおけるZICファミリーの発現が報告され、腫瘍化または腫瘍抑制における役割、診断・予後予測への応用が検討されている。肝細胞癌ではZIC2が転写因子OCT4の発現を活性化して、癌幹細胞の維持に関わることが報告された[35]。
| ヒトで遺伝的な関与がある疾患 | 遺伝子欠損マウスの症状 | |
| Zic1 | Dandy-Walker 奇形(小脳形成の異常) 頭蓋骨癒合症(狭頭症)・学習障害[32] |
小脳形成の異常 椎弓・肋骨形成の異常 筋緊張度の低下 |
| Zic2 | 全前脳症(HPE5、前脳正中部形成異常) 近視[36] [37] |
全前脳症・二分脊椎症様奇形 中軸・四肢骨格系形成の異常 筋肉発生の異常 大脳層構造の異常 視交叉での神経走向の異常 認知機能・社会行動の異常 髄膜の形成不全 |
| Zic3 | 内臓左右不定位症 (situs ambiguous, heterotaxy) 心奇形(内臓の左右位置異常と関係したもの、完全大動脈転位、両大血管右室起始症など) |
尾の屈曲、脊椎の形成異常 神経管奇形 左右軸形成の異常 小脳形成の異常 動眼調節機能の異常 筋緊張度の低下 |
参考文献
(2003年以前の文献は文献1-4の中に引用されている文献を参照)
- ↑
Aruga, J. (2004).
The role of Zic genes in neural development. Molecular and cellular neurosciences, 26(2), 205-21. [PubMed:15207846] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Grinberg, I., & Millen, K.J. (2005).
The ZIC gene family in development and disease. Clinical genetics, 67(4), 290-6. [PubMed:15733262] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Merzdorf, C.S. (2007).
Emerging roles for zic genes in early development. Developmental dynamics : an official publication of the American Association of Anatomists, 236(4), 922-40. [PubMed:17330889] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Houtmeyers, R., Souopgui, J., Tejpar, S., & Arkell, R. (2013).
The ZIC gene family encodes multi-functional proteins essential for patterning and morphogenesis. Cellular and molecular life sciences : CMLS, 70(20), 3791-811. [PubMed:23443491] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ 5.0 5.1
Aruga, J., Kamiya, A., Takahashi, H., Fujimi, T.J., Shimizu, Y., Ohkawa, K., ..., & Toyoda, A. (2006).
A wide-range phylogenetic analysis of Zic proteins: implications for correlations between protein structure conservation and body plan complexity. Genomics, 87(6), 783-92. [PubMed:16574373] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Hatayama, M., & Aruga, J. (2012).
Gli protein nuclear localization signal. Vitamins and hormones, 88, 73-89. [PubMed:22391300] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Kumano, G., Kawai, N., & Nishida, H. (2010).
Macho-1 regulates unequal cell divisions independently of its function as a muscle determinant. Developmental biology, 344(1), 284-92. [PubMed:20478299] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Murgan, S., Kari, W., Rothbächer, U., Iché-Torres, M., Mélénec, P., Hobert, O., & Bertrand, V. (2015).
Atypical Transcriptional Activation by TCF via a Zic Transcription Factor in C. elegans Neuronal Precursors. Developmental cell, 33(6), 737-45. [PubMed:26073017] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Sato, T., Sasai, N., & Sasai, Y. (2005).
Neural crest determination by co-activation of Pax3 and Zic1 genes in Xenopus ectoderm. Development (Cambridge, England), 132(10), 2355-63. [PubMed:15843410] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Klootwijk, R., Groenen, P., Schijvenaars, M., Hol, F., Hamel, B., Straatman, H., ..., & Franke, B. (2004).
Genetic variants in ZIC1, ZIC2, and ZIC3 are not major risk factors for neural tube defects in humans. American journal of medical genetics. Part A, 124A(1), 40-7. [PubMed:14679585] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Chabchoub, E., Willekens, D., Vermeesch, J.R., & Fryns, J.P. (2012).
Holoprosencephaly and ZIC2 microdeletions: novel clinical and epidemiological specificities delineated. Clinical genetics, 81(6), 584-9. [PubMed:21496007] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Warr, N., Powles-Glover, N., Chappell, A., Robson, J., Norris, D., & Arkell, R.M. (2008).
Zic2-associated holoprosencephaly is caused by a transient defect in the organizer region during gastrulation. Human molecular genetics, 17(19), 2986-96. [PubMed:18617531] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ 有賀純
Dandy−Walker症候群
Clinical Neuroscience, 2015. 33: p. 397-401. - ↑
Escalante, A., Murillo, B., Morenilla-Palao, C., Klar, A., & Herrera, E. (2013).
Zic2-dependent axon midline avoidance controls the formation of major ipsilateral tracts in the CNS. Neuron, 80(6), 1392-406. [PubMed:24360543] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Inoue, T., Ogawa, M., Mikoshiba, K., & Aruga, J. (2008).
Zic deficiency in the cortical marginal zone and meninges results in cortical lamination defects resembling those in type II lissencephaly. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 28(18), 4712-25. [PubMed:18448648] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Inoue, T., Ota, M., Mikoshiba, K., & Aruga, J. (2007).
Zic2 and Zic3 synergistically control neurulation and segmentation of paraxial mesoderm in mouse embryo. Developmental biology, 306(2), 669-84. [PubMed:17490632] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
D'Alessandro, L.C., Latney, B.C., Paluru, P.C., & Goldmuntz, E. (2013).
The phenotypic spectrum of ZIC3 mutations includes isolated d-transposition of the great arteries and double outlet right ventricle. American journal of medical genetics. Part A, 161A(4), 792-802. [PubMed:23427188] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Sutherland, M.J., Wang, S., Quinn, M.E., Haaning, A., & Ware, S.M. (2013).
Zic3 is required in the migrating primitive streak for node morphogenesis and left-right patterning. Human molecular genetics, 22(10), 1913-23. [PubMed:23303524] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Fujimi, T.J., Hatayama, M., & Aruga, J. (2012).
Xenopus Zic3 controls notochord and organizer development through suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Developmental biology, 361(2), 220-31. [PubMed:22056782] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Matsumoto, J., Kumano, G., & Nishida, H. (2007).
Direct activation by Ets and Zic is required for initial expression of the Brachyury gene in the ascidian notochord. Developmental biology, 306(2), 870-82. [PubMed:17459364] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Kanayama, M., Akiyama-Oda, Y., Nishimura, O., Tarui, H., Agata, K., & Oda, H. (2011).
Travelling and splitting of a wave of hedgehog expression involved in spider-head segmentation. Nature communications, 2, 500. [PubMed:21988916] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Janssen, R., & Budd, G.E. (2013).
Deciphering the onychophoran 'segmentation gene cascade': Gene expression reveals limited involvement of pair rule gene orthologs in segmentation, but a highly conserved segment polarity gene network. Developmental biology, 382(1), 224-34. [PubMed:23880430] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Takahashi, H., Shimizu, T., & Aruga, J. (2008).
Expression pattern of annelid Zic in embryonic development of the oligochaete Tubifex tubifex. Development genes and evolution, 218(10), 553-60. [PubMed:18810489] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Moriyama, Y., Kawanishi, T., Nakamura, R., Tsukahara, T., Sumiyama, K., Suster, M.L., ..., & Takeda, H. (2012).
The medaka zic1/zic4 mutant provides molecular insights into teleost caudal fin evolution. Current biology : CB, 22(7), 601-7. [PubMed:22386310] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Kawanishi, T., Kaneko, T., Moriyama, Y., Kinoshita, M., Yokoi, H., Suzuki, T., ..., & Takeda, H. (2013).
Modular development of the teleost trunk along the dorsoventral axis and zic1/zic4 as selector genes in the dorsal module. Development (Cambridge, England), 140(7), 1486-96. [PubMed:23462471] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Quinn, M.E., Haaning, A., & Ware, S.M. (2012).
Preaxial polydactyly caused by Gli3 haploinsufficiency is rescued by Zic3 loss of function in mice. Human molecular genetics, 21(8), 1888-96. [PubMed:22234993] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Pan, H., Gustafsson, M.K., Aruga, J., Tiedken, J.J., Chen, J.C., & Emerson, C.P. (2011).
A role for Zic1 and Zic2 in Myf5 regulation and somite myogenesis. Developmental biology, 351(1), 120-7. [PubMed:21211521] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Sawada, K., Fukushima, Y., & Nishida, H. (2005).
Macho-1 functions as transcriptional activator for muscle formation in embryos of the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi. Gene expression patterns : GEP, 5(3), 429-37. [PubMed:15661650] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ 29.0 29.1
Hatayama, M., Ishiguro, A., Iwayama, Y., Takashima, N., Sakoori, K., Toyota, T., ..., & Aruga, J. (2011).
Zic2 hypomorphic mutant mice as a schizophrenia model and ZIC2 mutations identified in schizophrenia patients. Scientific reports, 1, 16. [PubMed:22355535] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Xu, Y., Yao Shugart, Y., Wang, G., Cheng, Z., Jin, C., Zhang, K., ..., & Zhang, D. (2016).
Altered expression of mRNA profiles in blood of early-onset schizophrenia. Scientific reports, 6, 16767. [PubMed:26733343] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Aruga, J., Ogura, H., Shutoh, F., Ogawa, M., Franke, B., Nagao, S., & Mikoshiba, K. (2004).
Locomotor and oculomotor impairment associated with cerebellar dysgenesis in Zic3-deficient (Bent tail) mutant mice. The European journal of neuroscience, 20(8), 2159-67. [PubMed:15450095] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑ 32.0 32.1
Twigg, S.R., Forecki, J., Goos, J.A., Richardson, I.C., Hoogeboom, A.J., van den Ouweland, A.M., ..., & Wilkie, A.O. (2015).
Gain-of-Function Mutations in ZIC1 Are Associated with Coronal Craniosynostosis and Learning Disability. American journal of human genetics, 97(3), 378-88. [PubMed:26340333] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Lim, L.S., Loh, Y.H., Zhang, W., Li, Y., Chen, X., Wang, Y., ..., & Stanton, L.W. (2007).
Zic3 is required for maintenance of pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Molecular biology of the cell, 18(4), 1348-58. [PubMed:17267691] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Luo, Z., Gao, X., Lin, C., Smith, E.R., Marshall, S.A., Swanson, S.K., ..., & Shilatifard, A. (2015).
Zic2 is an enhancer-binding factor required for embryonic stem cell specification. Molecular cell, 57(4), 685-694. [PubMed:25699711] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Zhu, P., Wang, Y., He, L., Huang, G., Du, Y., Zhang, G., ..., & Fan, Z. (2015).
ZIC2-dependent OCT4 activation drives self-renewal of human liver cancer stem cells. The Journal of clinical investigation, 125(10), 3795-808. [PubMed:26426078] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Verhoeven, V.J., Hysi, P.G., Wojciechowski, R., Fan, Q., Guggenheim, J.A., Höhn, R., ..., & Hammond, C.J. (2013).
Genome-wide meta-analyses of multiancestry cohorts identify multiple new susceptibility loci for refractive error and myopia. Nature genetics, 45(3), 314-8. [PubMed:23396134] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Oishi, M., Yamashiro, K., Miyake, M., Akagi-Kurashige, Y., Kumagai, K., Nakata, I., ..., & Yoshimura, N. (2013).
Association between ZIC2, RASGRF1, and SHISA6 genes and high myopia in Japanese subjects. Investigative ophthalmology & visual science, 54(12), 7492-7. [PubMed:24150758] [WorldCat] [DOI] - ↑
Hilger, A.C., Halbritter, J., Pennimpede, T., van der Ven, A., Sarma, G., Braun, D.A., ..., & Hildebrandt, F. (2015).
Targeted Resequencing of 29 Candidate Genes and Mouse Expression Studies Implicate ZIC3 and FOXF1 in Human VATER/VACTERL Association. Human mutation, 36(12), 1150-4. [PubMed:26294094] [PMC] [WorldCat] [DOI]